Figure 5.
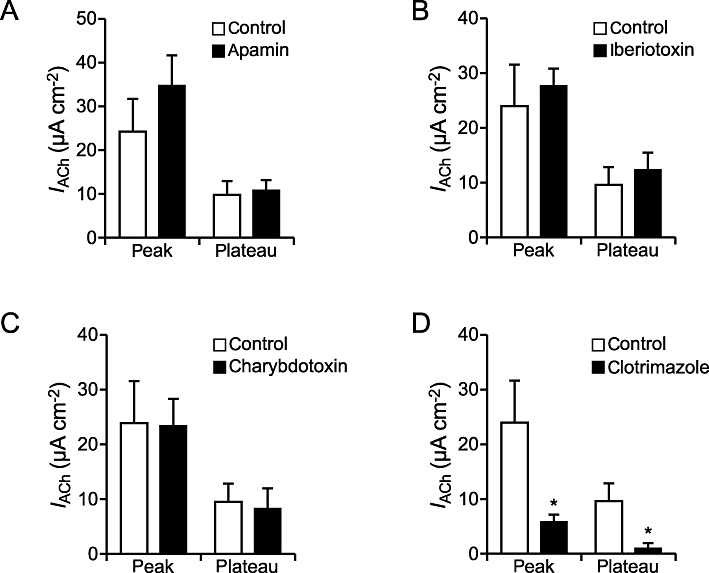
Influence of inhibitors of Ca2+ dependent K+ channels on the ACh effect. (A) The presence of the KCa2.1, KCa2.2 and KCa2.3 channel inhibitor apamin (2 µM, basolateral, n= 5) resulted in an unchanged ACh-induced current increase compared with control conditions (n= 7) (peak: P= 0.31, plateau: P= 0.80). (B) The ACh-induced current (IACh) in the presence of the KCa1.1 channel inhibitor iberiotoxin (250 nM, basolateral, n= 5) was not significantly different from the control effect (n= 7) (peak: P= 0.65, plateau: P= 0.56). (C) In the presence of the KCa1.1 and KCa3.1 channel inhibitor charybdotoxin (200 nM, basolateral, n= 5) the ACh-induced current was not significantly altered compared with the control effect (n= 7) (peak: P= 0.94, plateau: P= 0.77). (D) Both components of the ACh effect in the presence of the KCa3.1 channel inhibitor clotrimazol (n= 5) were significantly reduced (P≤ 0.05) compared with the control ACh effect (n= 7).
