Figure 1.
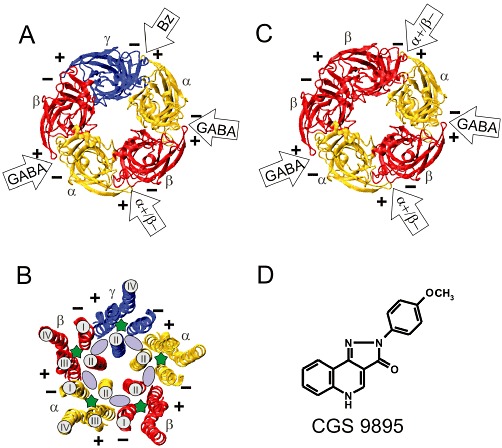
Model structures of the extracellular and transmembrane domains of GABAA receptors and chemical structure of CGS 9895. (A) Extracellular domain or (B) transmembrane domain of a GABAA receptor composed of one γ, two α and two β subunits. (C) Extracellular domain of a GABAA receptor composed of two α and three β subunits. (A, B, C) The structures are shown in ribbon representation and are viewed from the extracellular side. The plus (+) and the minus (−) side of each subunit is indicated. The two GABA sites are located at the β+α− interfaces, and the benzodiazepine (BZ) binding site is located at the α+γ− interface. (B) Solvent accessible space contained in the transmembrane domain of GABAA receptor models. The intra-subunit pockets are located within the four helix transmembrane domains and are marked with a green asterisk. Only helix II is marked in all subunits. Helices I–IV are only marked for a single β and an α subunit. The inter-subunit pockets are indicated by a light purple ellipse and are located between helices II and III of one subunit (+ side) and helices II and I of a neighbouring subunit (− side). (D) Chemical structure of CGS 9895.
