Figure 3.
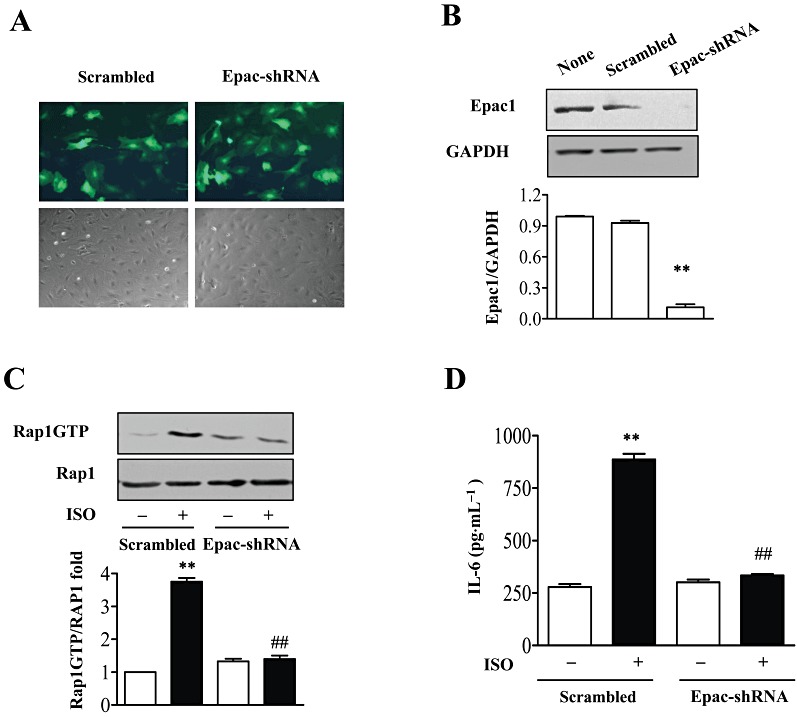
Inhibition of Epac repressed β-adrenoceptor-induced IL-6 secretion. (A) The infection efficiency of NMCFs with adenovirus expressing Epac-shRNAs or scrambled RNA for 48 h. Green, GFP inflorescence. (B) Effect of Epac-shRNAs on Epac protein levels. Cells were infected with adenovirus expressing Epac-shRNAs or scrambled RNA for 48 h. Cell lysates were immunoblotted with Epac antibody or GAPDH as loading control. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. **P < 0.01, PKCδ-shRNA vs. scrambled, n= 3. (C) Effect of Epac-shRNA on Rap1 activity after isoprenaline (ISO) by using GST-RalGDS-Ras binding domain as an activation-specific probe. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. **P < 0.01 vs. control, ##P < 0.01 PKCδ-shRNAs vs. scrambled, n= 3. (D) NMCFs were infected with adenovirus expressing Epac-shRNAs or scrambled RNAs for 48 h, then stimulated with isoprenaline (10 µM) for 12 h. IL-6 in the supernatant was determined by ELISA. **P < 0.01 vs. control, ##P < 0.01 PKCδ-shRNAs vs. scrambled, n= 3.
