Figure 2.
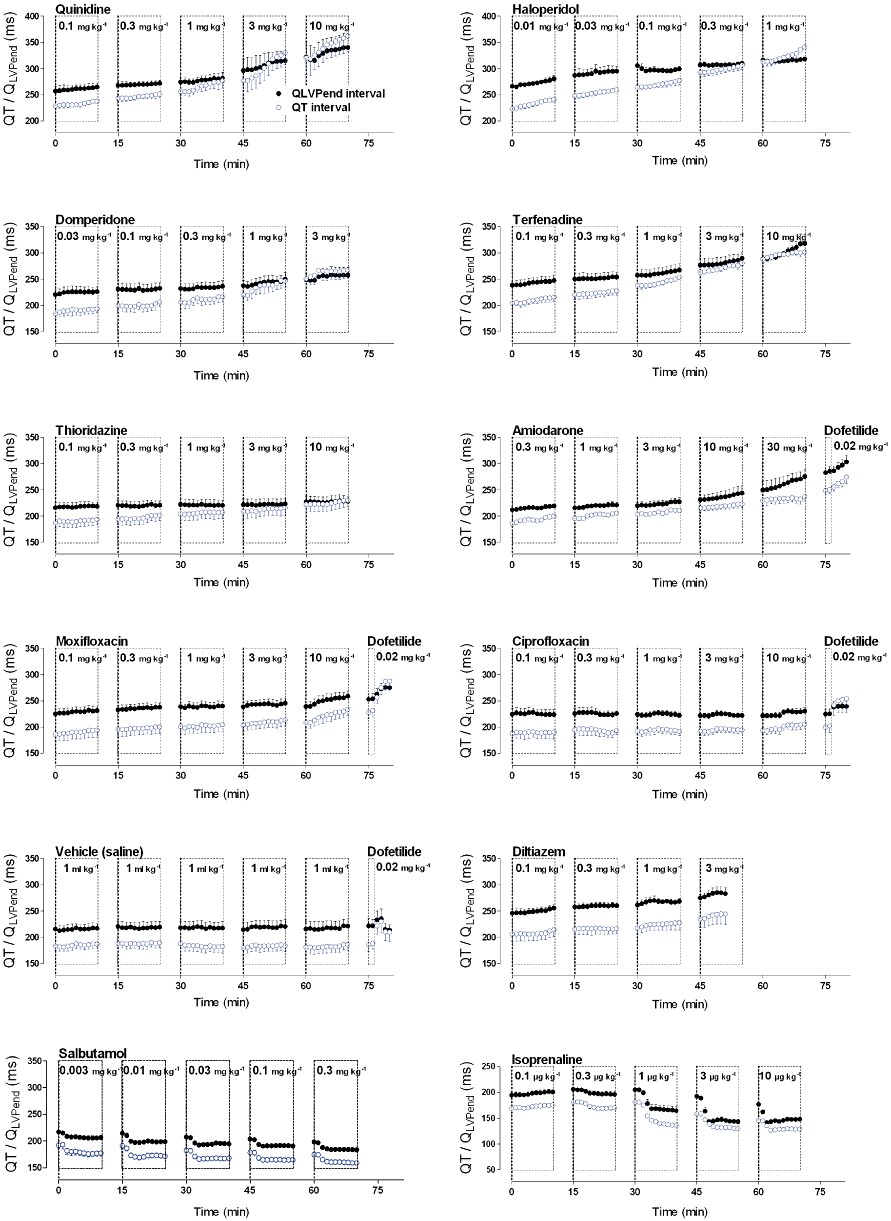
Graphs show the effect of various pharmacological agents on the electro-mechanical coupling in anaesthetized guinea pigs. Drugs with high TdP risk (quinidine, haloperidol, domperidone, terfenadine, dofetilide and thioridazine) induced unequal changes of the QT interval versus the QLVPend interval, whereas drugs with low (amiodarone, moxifloxacin and ciprofloxacin), or no TdP risk (vehicle, salbutamol and diltiazem) induced parallel changes of the QT interval and LVPend interval. Finally, isoprenaline showed different kinetics of its effect on the QT and QLVPend interval leading to a transient decrease of the E-M window. Plots show mean ± SEM.
