Figure 1.
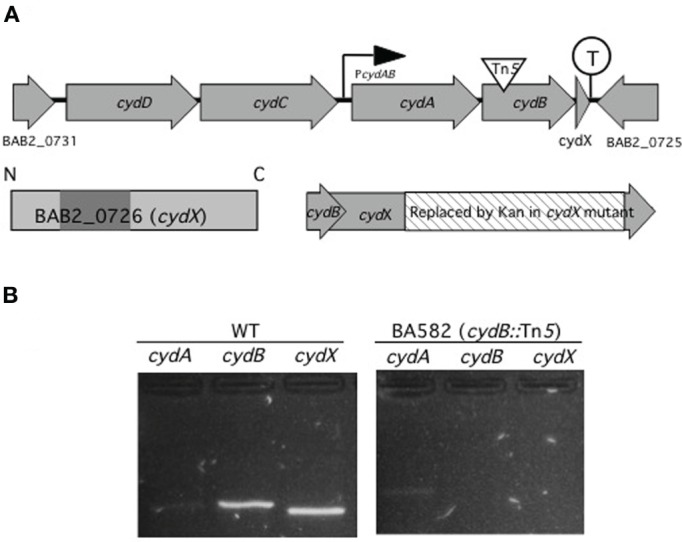
cydA, cydB, and cydX are organized and transcribed as a gene cluster. (A) Genetic map of the cyd locus in B. abortus 2308 chromosome II. cydA and cydB encode two proteins with similarity to subunit I and II of cytochrome bd-1 terminal oxidase in E. coli. Upstream of cydA and cydB are two predicted ABC transporter genes with similarity to E. colicydD and cydC. Overlapping 23 bp with cydB, cydX encodes a 64 aa protein with one predicted transmembrane domain (shaded), spanning residues 17–35. While no promoter is predicted in front of cydD there is a promoter (PcydAB), possibly driving transcription of cydA, cydB, and cydX. A transcriptional terminator (circled T) is located between cydX and its adjacent open reading frame BAB2_0725. In BA582 (cydB::Tn5) a transposon is inserted in cydB (triangle) while in cydX::Kan part of cydX (hatched) is replaced by a kanamycin resistance determinant without disrupting cydB. (B) Analysis of the cyd gene cluster by RT-PCR. PCR products for the indicated primers with wild type (WT) or cydB::Tn5 mutant (BA582) as a template are shown. The sizes of the predicted amplicons for cydA, cydB, and cydX are 247 bp, 243 bp, and 204 bp, respectively. Control reactions in which reverse transcriptase were omitted had no amplification product (not shown).
