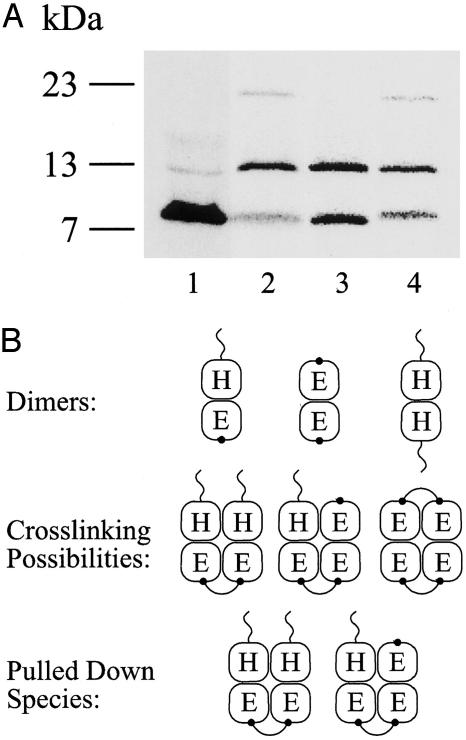
Fig. 6.
Crosslinking of CLA-EmrE-His/K22C heterodimers. (A) CLA-EmrE-His/K22C heterodimers were generated in vitro by coexpressing both proteins. K22C was expressed in excess to optimize formation of heterodimers over CLA-EmrE-His homodimers. A sample (0.5 μl) was separated by SDS/PAGE immediately after in vitro-synthesis reaction was completed. K22C was expressed in large excess compared with CLA-EmrE-His (lane 1). A 20-μl sample was bound to Ni-NTA beads immediately after synthesis was completed (lane 3) or dialyzed against 0.08% DDM/Na buffer and crosslinked with o-PDM (lane 2). Final o-PDM concentration was 400 μM. The reaction was stopped after 1 h at room temperature with 15 mM 2-mercaptoethanol, loaded on Ni-NTA beads, washed, and eluted, as described in Experimental Procedures. A sample of the eluted protein was then separated by SDS/PAGE (lane 2). An identical untreated sample was bound to Ni-NTA beads, and crosslinking with o-PDM was performed, whereas the protein was already bound to beads as described in Experimental Procedures (lane 4). (B) Schematic representation of the forms of the dimers, crosslinking possibilities, and pulled-down species. H, EmrE-His; E, EmrE-CLA-K22C. The “tail” on the H subunit symbolizes the His-tag, and the dot on EmrE-CLA-K22C stands for the crosslinking site (K22C).