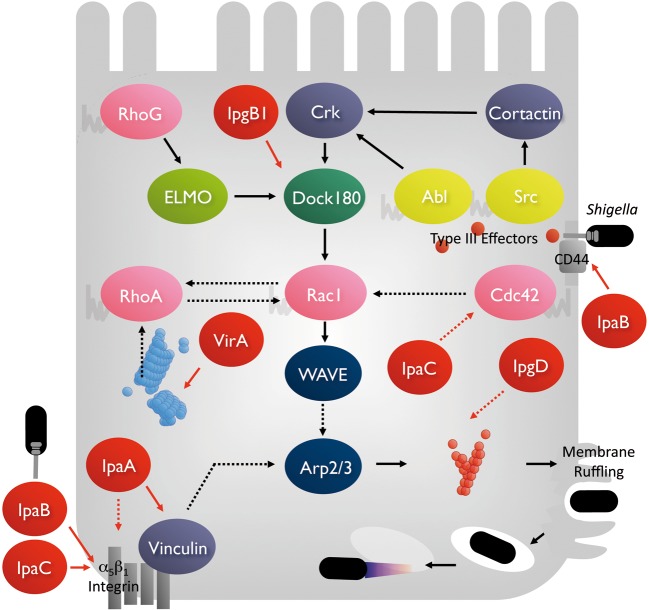
Fig. 4.
A model of Shigella invasive mechanism for epithelial cells. Upon contact of Shigella to epithelial cells, the bacterium delivers several effectors (red circles) via the TTSS around the bacterial surface and into the host-cell cytoplasm. The bacterial effectors interact with the host target molecules to stimulate several signal transduction pathways capable of activating the Rac1-WAVE-Arp2/3 pathway, and induce local actin polymerization and protrude the membrane ruffles. See the text for details.