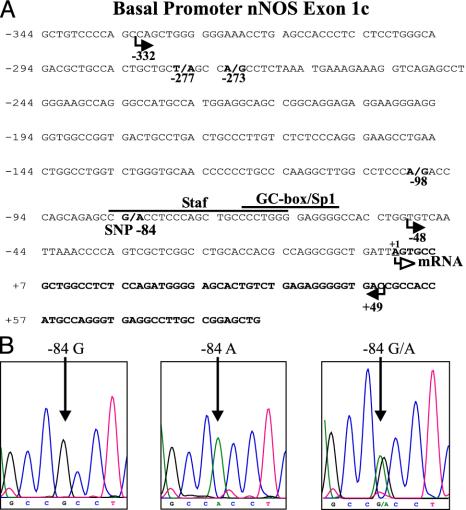
Fig. 2.
Mutations and polymorphisms in the nNOS exon 1c promoter in patients with IHPS. (A) Nucleotide sequence of human nNOS exon 1c (bold) and in part of the 5′-flanking region including the minimal promoter. The transcription start site is indicated as +1. Cis-acting elements previously determined by gel-shift assays and site-directed mutagenesis (25) are indicated by the lines above the sequence. Mutations (-277T → A, -273A → G, and -98A → G) detected in DNA probes of IHPS patients and the -84G/A SNP are shown in bold and numbered below the sequence relative to the transcription start site (+1). Arrows below the nucleotide sequence depict the 5′-deletion sites of the different nNOS pGL3 promoter constructs used in reporter gene assays (Fig. 3). (B) DNA sequence analysis of the nNOS exon 1c -84G/A SNP. (Left) G/G homozygous DNA. (Center) A/A homozygous DNA. (Right) G/A heterozygous DNA. The position of nucleotide -84 is indicated with an arrow.