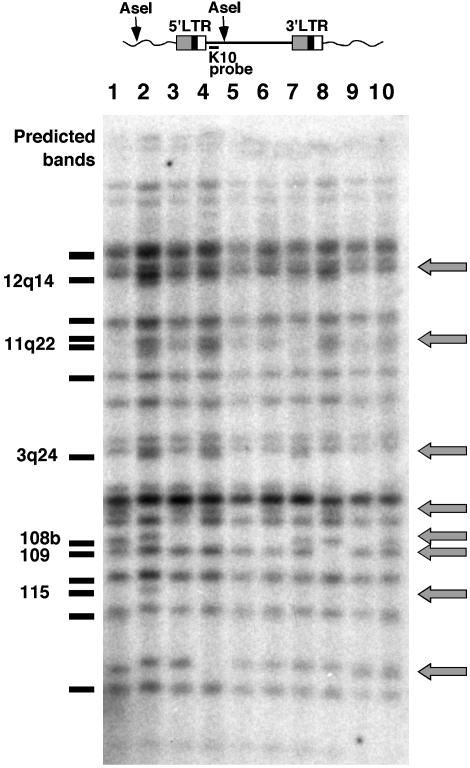
Fig. 1.
Detection of HERV-K polymorphisms. (Upper) The position of the K10 oligonucleotide probe and putative Ase I sites relative to a typical HERV-K element. (Lower) Unblotting of a set of human genomic DNA samples digested with Ase I and probed with K10. Gray arrows indicate bands that are polymorphic within the sample. Bands predicted from the genomic database are plotted to the left of the blot, and the bands that appear to be polymorphic are indicated. Five of these elements have been identified: HERV-K108, 109, and 115 (9, 11); and HERV-K11q22 and 12q14 (29). The HERV-K element 3q24 is not full-length and was identified in the clone with GenBank accession no. AC069410 (Human Bacterial Artificial Chromosome Library, Roswell Park Cancer Institute, Buffalo, NY). The band marked 108b is the size expected for the central LTR of the tandem form of HERV-K 108 (20) (see Fig. 2).