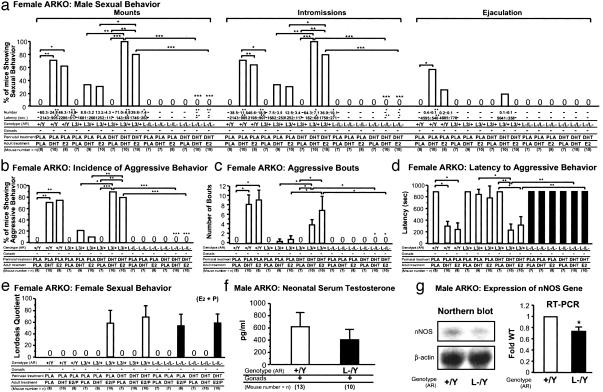
Fig. 4.
Failure of ARL-/L- mice to express male-typical behaviors after DHT-induced perinatal brain masculinization. (a) WT female mice, but not ARL-/L- mice, showed male sexual behaviors in response to either DHT or E2 treatment as adults after perinatal exposure to DHT. Behavioral tests were performed as described in Fig. 2a. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. (b) Percentage of mice exhibiting aggressive behaviors (incidence of male aggressive behavior) toward olfactory bulbectomized (OBX) male intruder mice. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. (c) Number of bouts with attacks. *, P < 0.05. (d) Latency to the first attack during resident–intruder tests. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. (e) Expression of female sexual behaviors is independent of AR/androgen signaling during the perinatal stage. Behavioral tests were performed after E2 and progesterone treatment (E2/P) as described in Fig. 2e. (f) No clear reduction in serum testosterone levels in ARL-/Y neonate mice (1 day after birth). (g) Reduced expression levels of nNOS transcript in ARL-/Y hypothalamus by Northern blot analysis. Densitometric analysis of the relative expression level by semiquantitative RT-PCR, expressed as fold WT after normalization to GAPDH. *, P < 0.05.