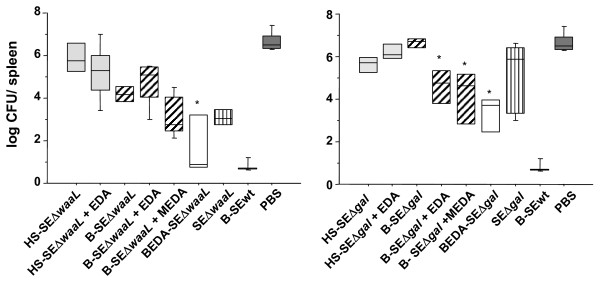
Figure 4.
Protection conferred by antigenic preparations fromSalmonellaEnteritidis rough mutants in BALB/c mice. Immunizations. (A) SEΔwaaL immunizations; and (B) SEΔgal immunizations. Mice were immunized IP with hot saline (HS) extracts (HS-SEΔwaaL and HS-SEΔgal; grey boxes), formalin inactivated bacterins (B-SEΔwaaL and B-SEΔgal; grey line boxes), alone, in combination with EDA (+EDA) or MEDA (+MEDA), or as biotinylated bacterins bound to EDAvidin (BEDA-SEΔwaaL and BEDA-SEΔgal; white boxes). Control groups of mice (n = 4) received live rough mutants (SEΔwaaL or SEΔgal, vertical line boxes), either HS or bacterin obtained from Salmonella Enteritidis parental strain (represented as B-SEwt; black boxes) or PBS (black boxes). Four weeks after vaccination, all mice were challenged IP with 2.3 × 102 CFU of Salmonella Enteritidis strain 3934 (SE-wt) per animal and the degree of protection expressed as the mean log10 CFU/spleen of SE-wt, at day 4 after challenge. Statistical comparisons were performed by ANOVA and Fisher’s PLSD test. * P < 0.01 for differences with the corresponding bacterin administered alone, i.e. BEDA-SEΔwaaL vs. B-SEΔwaaL; and BEDA-SEΔgal or B-SEΔgal plus EDA/MEDA vs. B-SEΔgal.