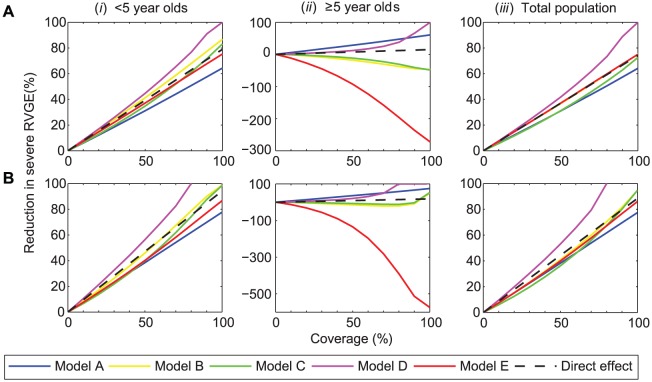
Figure 4. Long-term impact of vaccination on the incidence of severe RVGE predicted by the models.
The reduction in the incidence of severe RVGE during a 10-year period beginning 10 years after vaccine introduction, as compared to the mean pre-vaccination incidence, is plotted for coverage levels from 0 to 100%. The panels represent the reduction in incidence of severe RVGE under (A) scenario 1: vaccination is assumed to confer immunity comparable to primary infection following the first dose at 2 months of age (82% efficacy), and (B) scenario 2: vaccination is assumed to confer immunity comparable to one natural infection following each dose at 2 and 4 months of age (99% efficacy), for (i) <5 years of age, (ii) ≥5 years of age, and (iii) all age groups. Black dashed lines represent the direct effect of vaccination (see Text S1), while solid colored lines represent the model projections: Model A (blue), Model B (yellow), Model C (green), Model D (purple), Model E (red).