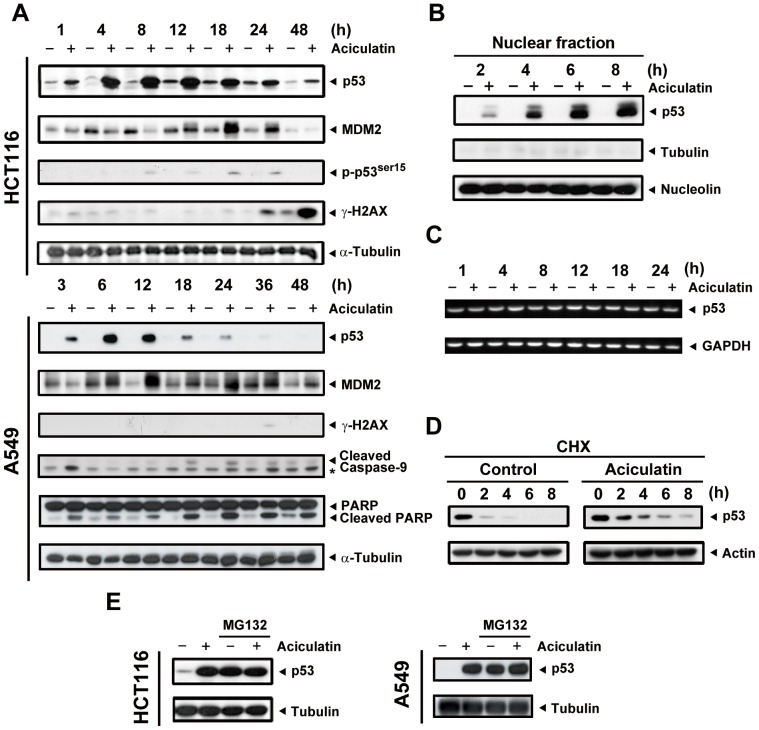
Figure 3. Accumulation of p53 is observed following aciculatin treatment in HCT116 and A549 cells via a proteasome degradation pathway.
A, HCT116 and A549 cells were treated with aciculatin (10 µM) for the indicated periods and then harvested for detection of p53-related proteins. The levels of p53, phospho-ser15-p53, γ-H2AX, and the p53 downstream target MDM2 were then determined in HCT116 cells. The levels of p53, MDM2, γ-H2AX, cleaved caspase-9 and PARP were determined in A549 cells. The star marks a non-specific band. B, Nuclear extraction of HCT116 cells was performed after aciculatin treatment at the indicated time points. Aciculatin-induced nuclear accumulation of p53 was shown to be time-dependent. C, HCT116 cells were treated with aciculatin (10 µM) at different time points followed by extraction of total RNA. The p53 mRNA was co-amplified with GAPDH. D, HCT116 cells were pretreated with aciculatin (10 µM) for 3 h, followed by treatment with cycloheximide (20 µg/ml) with or without aciculatin (10 µM) for the indicated periods. E, HCT116 and A549 cells were co-treated with 10 µM MG132 and 10 µM aciculatin for 6 h and then harvested for p53 detection by immunoblotting.