FIGURE 3:
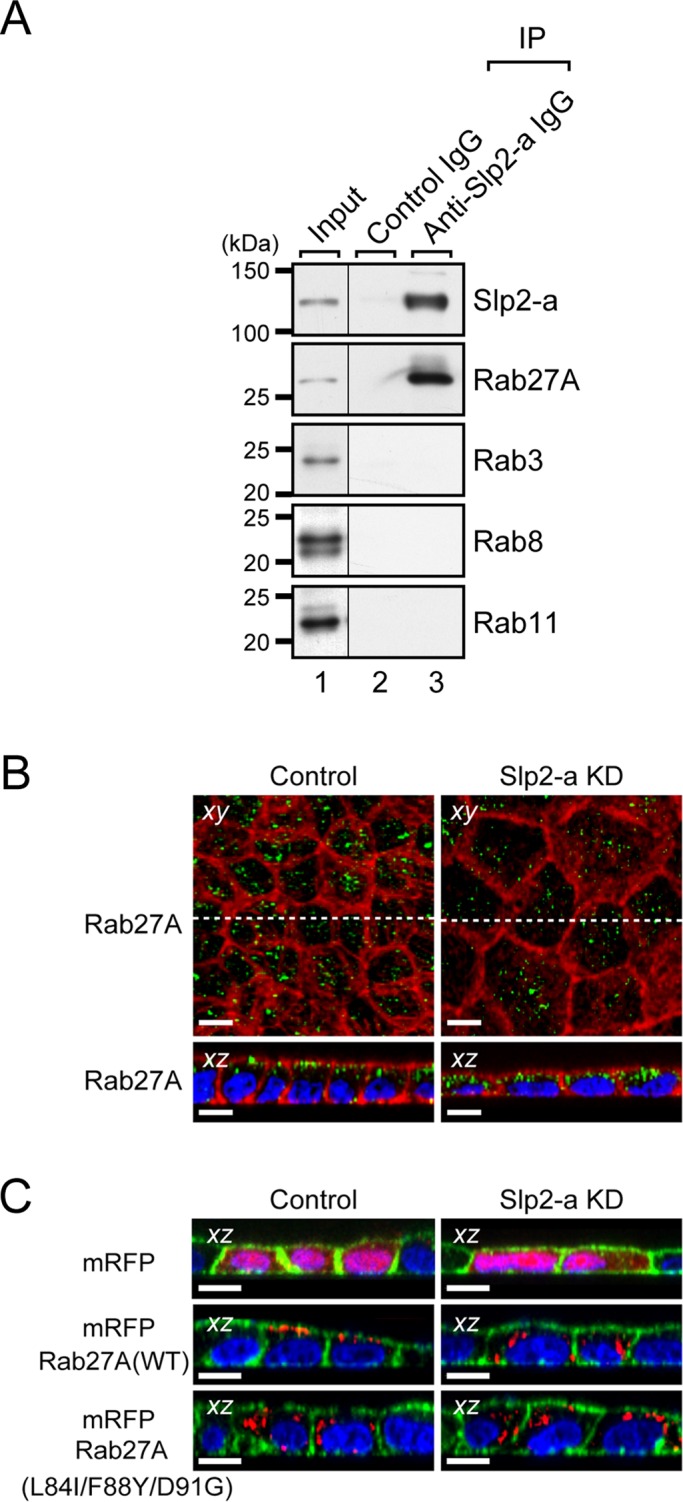
Slp2-a is required for the apical membrane localization of Rab27A in MDCK II cells. (A) Endogenous interaction between Slp2-a and Rab27A in MDCK II cells. Total cell lysates of confluent MDCK II cells were coimmunoprecipitated with anti–Slp2-a antibody and subjected to 10% SDS–PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with the antibodies indicated on the right. Note that Slp2-a interacted with Rab27A alone and not with any of the other Rabs tested. The positions of the molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are shown on the left. (B) Altered cellular localization of Rab27A in Slp2-a KD cells. Confluent control cells and Slp2-a KD cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with Texas red–conjugated phalloidin (red) and anti-Rab27A antibody (green). Although Rab27A was preferentially localized at the apical membrane in the control cells, the apical membrane localization of Rab27A was decreased in the Slp2-a KD cells. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 10 μm. (C) Requirement of Slp2-a binding of Rab27A for apical membrane localization. Control cells and Slp2-a KD cells were transfected with pmRFP-C1, pmRFP-C1-Rab27A(WT), or pmRFP-C1-Rab27A(L84I/F88Y/D91G). Two days after transfection, the cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with Alexa Fluor 488–conjugated phalloidin (green) and DAPI (blue). Although mRFP-Rab27A(WT) was preferentially localized at the apical membrane, the mutant protein was dispersed throughout the cytoplasm in the control cells (left, red). By contrast, both mRFP-Rab27A(WT) and mRFP-Rab27A(L84I/F88Y/D91G) were dispersed throughout the cytoplasm in the Slp2-a KD cells (right, red). Top, the cytosolic localization of control mRFP alone both in the control cells and in the Slp2-a KD cells. Scale bars, 10 μm.
