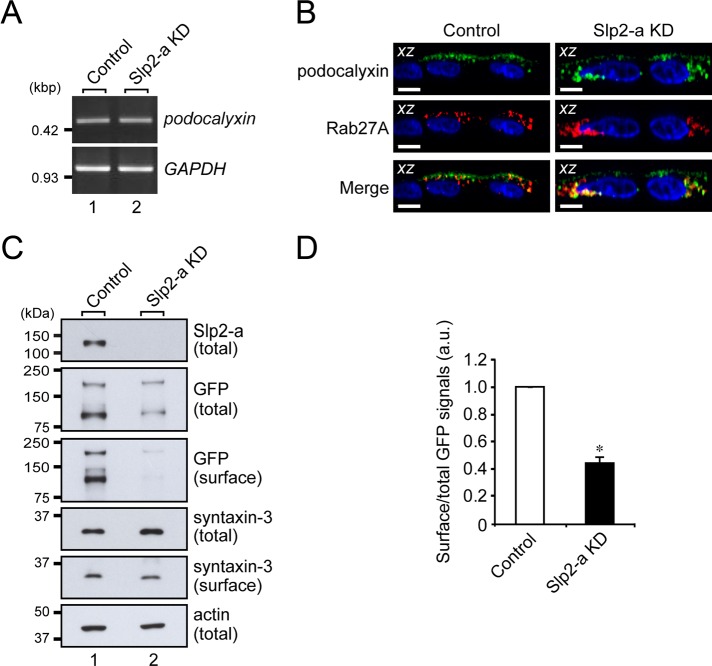
FIGURE 4:
Slp2-a is involved in the apical targeting of podocalyxin in MDCK II cells. (A) Unaltered expression of podocalyxin mRNA in Slp2-a KD cells as demonstrated by RT-PCR analysis. The level of podocalyxin mRNA expression in the control cells and the Slp2-a KD cells was the same. GAPDH was used as an internal control. The size of the molecular weight markers (kilobase pairs [kbp]) is shown on the left. (B) Colocalization of Rab27A and podocalyxin in the intracellular compartment. Control cells and Slp2-a KD cells were transfected with a podocalyxin-Venus expression vector and pmRFP-C1-Rab27A, and 2 d after transfection, the cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with DAPI (blue). Podocalyxin (green) and Rab27A (red) were partially colocalized at the apical membrane and in the cytoplasm even in the absence of Slp2-a (yellow dots). Although podocalyxin (left, green) was preferentially localized at the apical membrane in the control cells, podocalyxin was dispersed throughout the cytoplasm in the Slp2-a KD cells (top right, green), the same as Rab27A protein was (middle right, red). Scale bars, 10 μm. (C) Reduced surface podocalyxin expression in Slp2-a KD cells. Control cells and Slp2-a KD cells were transfected with a podocalyxin-Venus expression vector, and 2 d after transfection, total cell lysates and surface biotinylated proteins were subjected to 10% SDS–PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with the antibodies indicated on the right. Actin was used as an internal control. The positions of the molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are shown on the left. (D) Quantification of GFP (podocalyxin-Venus) signals shown in C. Note that the level of podocalyxin-Venus expression at the apical membrane was significantly decreased in the absence of Slp2-a, whereas the level of syntaxin-3 at the apical membrane was about the same. Data are expressed as the means ± SEM of three independent experiments. *p < 0.01 (Student's unpaired t test). a.u., arbitrary units.