FIGURE 5:
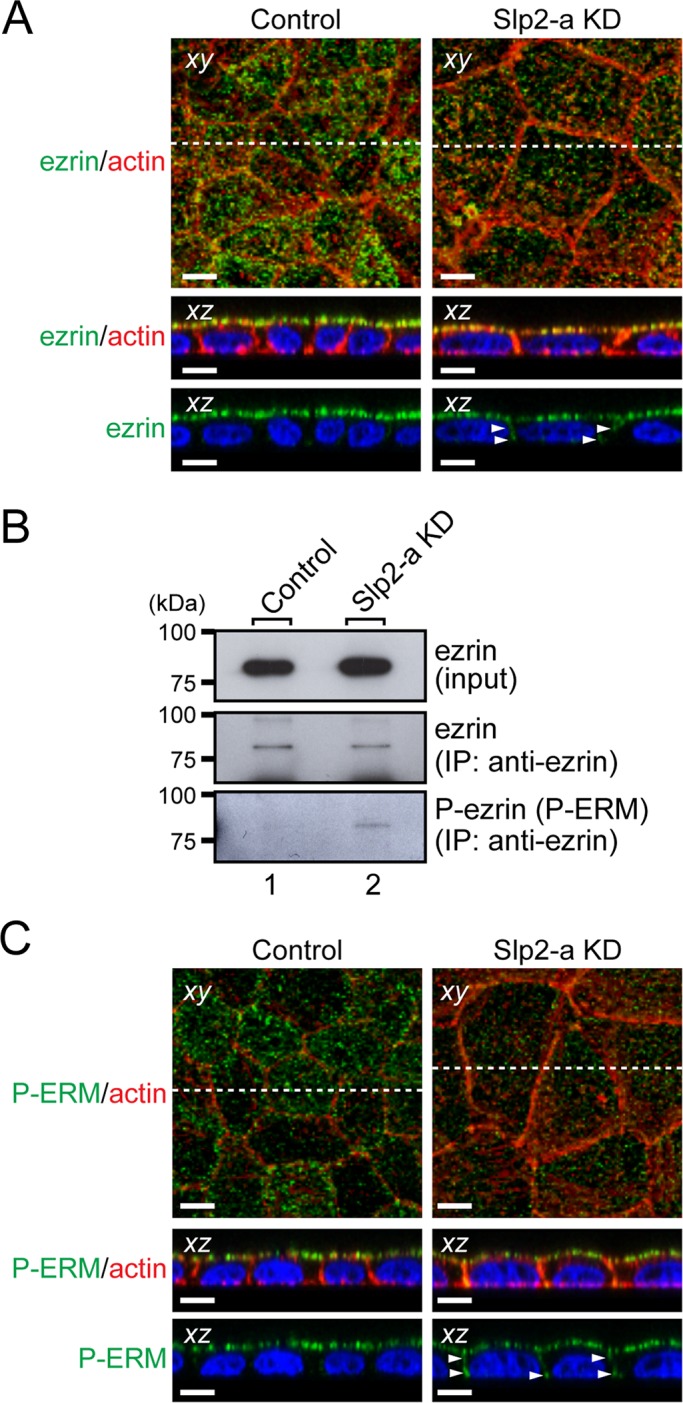
Ezrin, a downstream target of podocalyxin, is activated in Slp2-a KD cells. (A) Altered cellular localization of ezrin in Slp2-a KD cells. Confluent control cells and Slp2-a KD cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with anti-ezrin antibody (green) and Texas red–conjugated phalloidin (red). Ezrin was almost exclusively localized at the apical membrane in the control cells, whereas even though ezrin was preferentially localized at the apical region in the Slp2-a KD cells, ezrin was also localized at the basolateral membrane (arrowheads). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 10 μm. (B) Increased phosphorylation of ezrin in Slp2-a KD cells. Total cell lysates of confluent control cells and Slp2-a KD cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-ezrin antibody and subjected to 10% SDS–PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with the antibodies indicated on the right. The phosphorylation level of ezrin in the Slp2-a KD cells was much higher than in the control cells, whereas the level of ezrin expression appeared to be the same. The positions of the molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are shown on the left. (C) Phosphorylation of ERM proteins at the plasma membrane. Confluent control cells and Slp2-a KD cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with anti–phospho-ERM antibody (P-ERM; green) and Texas red–conjugated phalloidin (actin; red). Immunoreactive signals of phospho-ERM were observed at the apical membrane in the control cells, the same as those of ezrin, whereas in the Slp2-a KD cells immunoreactive signals of phospho-ERM were also observed at both the apical membrane and the basolateral membrane (arrowheads). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 10 μm.
