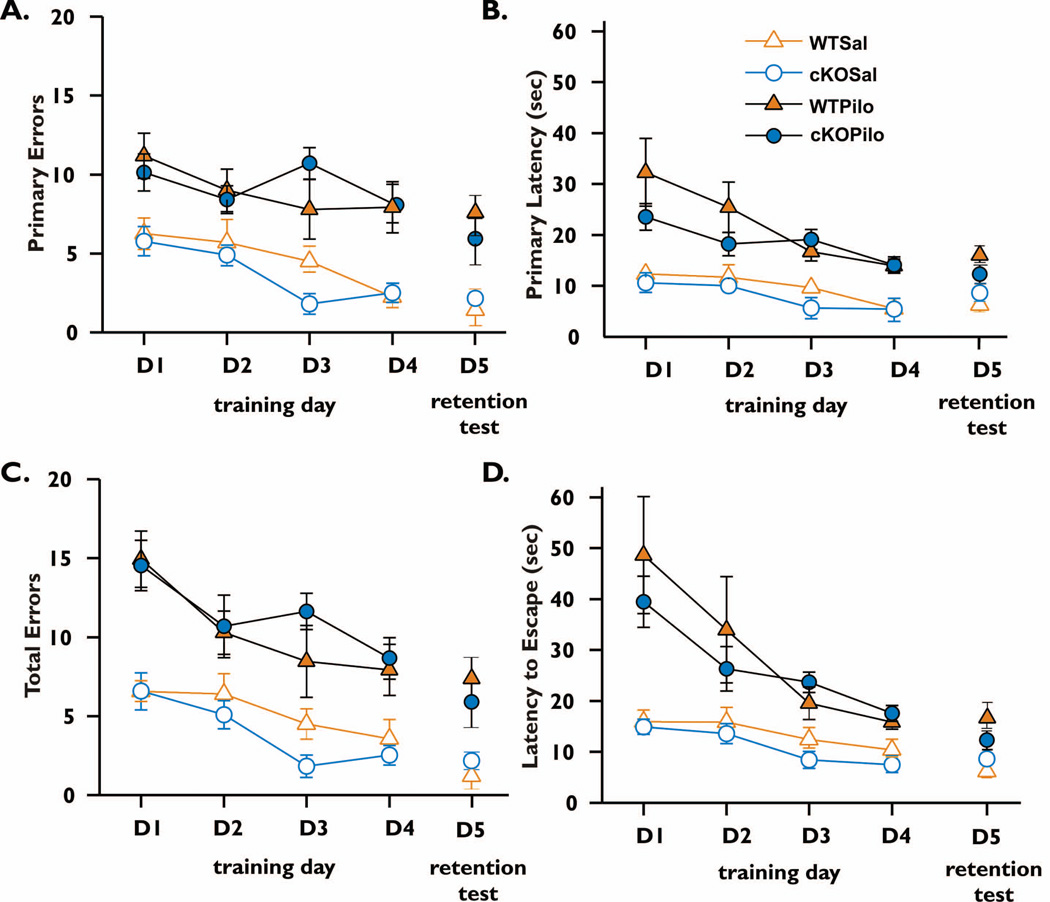
Figure 5. Barnes maze performance after SE.
For each of four days of training performed 21 days after pilocarpine, mice were subjected to four 3-minute trials in the maze as in Figure 1, and the data for all four trials were averaged for each mouse. After 4 days of training, on day 5 the target hole was covered to assess retention of spatial memory and mice were allowed to explore the maze during two 90 sec trials. The number of error holes explored before reaching the target hole (A), the latency to first reach the target hole (B), the total number of errors made before escaping into the target hole (C) and the time required to escape into the target hole (D) were measured. Data represent mean (±SEM) of four trials per day for D1–D4 and two trials on D5. Animals of both genotypes performed more poorly on all measures when treated with pilocarpine compared with saline (main effect of treatment in panel A WT, F=16.7, p=0.0013; panel A cKO F=65.6, p<0.0001; panel B WT F=16.7, p=0.0013; cKO F=45.9, p<0.0001; panel C WT, F=13.6, p=0.0027; cKO F=45.7, p<0.0001; panel D WT F=8.23, p=0.0132; cKO F=35.8, p<0.0001). Both genotypes performed similarly under both treatments (main effect of genotype Sal (A) F=1.592, p=0.2045; (B) F=0.7261, p=0.5417; (C) F=1.326, p=0.2777; (D) F=0.3587, p=0.7831; for pilocarpine (A) F=0.8554, p=0.4707; (B) F=2.064, p=0.1174; (C) F=0.4742, p=0.7017; (D) F=1.053, p=0.3777). A significant interaction between genotype and treatment was found on training day 3 for both primary errors (panel A, F=6.59, p=0.0153) and total errors made (panel C, F=5.36, p=0.0274). However, for other training days there was no interaction between treatment and genotype for any measure (panel A, F ranged from 0.00 to 0.02 and p ranged from 0.886 to 0.993; panel B, F=0.08 to 3.03 and p=0.092 to 0.777; panel C, F=0.02 to 0.53 and p= 0.474 to 0.887; panel D, F=0.26 to 3.69 and p=0.064 to 0.616). There was a strong main effect of training day under all conditions (in panels A-D, F ranged from 3.08 to 11.0 and p ranged from 0.0385 to <0.0001), except for panel A cKO mice treated with pilocarpine (F=2.63, p=0.0590), indicating that mice learned the maze at a similar rate. On D5, the retention trial, the WT Pilocarpine group made significantly more errors and took longer to locate the original escape hole location compared to their respective saline group (A/C,B/D). nCOX-2 cKO mice showed a trend to poorer performance after pilocarpine compared to control, but this did not reach significance (panels A/C,B/D). There was no interaction between treatment and genotype in the retention test: A, F=0.873, p=0.357; B, F=3.380, p=0.076. WT Saline n=8, nCOX-2 cKO Saline n=9, WT Pilocarpine n=7, and nCOX-2 cKO Pilocarpine n=11.