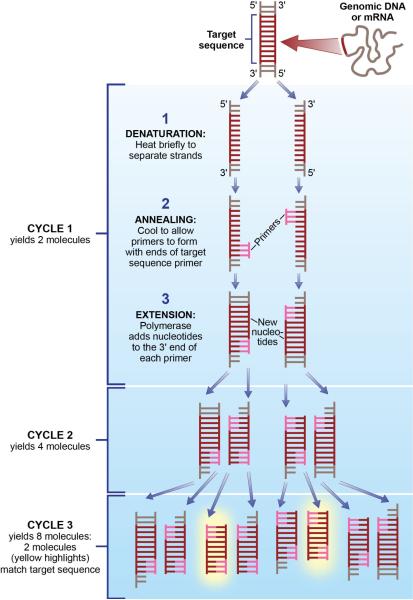
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of polymerase chain reaction (PCR). There are three major steps in a PCR, which can be repeated for 30 or 40 cycles – denaturation, annealing and extension. Because both strands are copied during PCR, there is an exponential increase of the number of copies of the gene. For example, if there is only one copy of the wanted gene before the cycling starts, after one cycle, there will be 2 copies, after two cycles, there will be 4 copies, three cycles will result in 8 copies and so on. Adapted from Lawley, R. A revolution in the microbiology laboratory. Retrived July 2011 from http://www.foodsafetywatch.com/public/1050