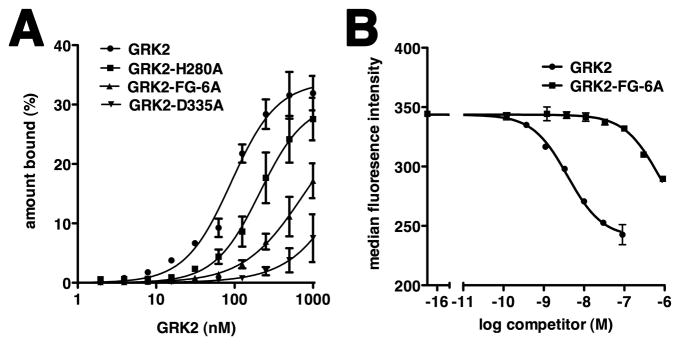
Figure 3. GRK2 Residues His280, Asp335 and the Basic αF-αG Loop Contribute to C13 Binding.
(A) Filter retention analysis of the relative amount of radioactively labeled C13 bound to wild-type GRK2 or its mutants. Results are plotted as a function of protein concentration, as described in Figure 2B. The Kd ± SEM for C13 binding to wild-type GRK2 or GRK2 H280A was 91 ± 11 nM and 211 ± 55 nM, respectively. Weaker affinity was observed for C13 binding to GRK2 FG-6A. The interaction of C13 with GRK2 D335A was barely detectable. Data represent at least two independent experiments.
(B) Mutation of basic residues in the αF-αG loop of GRK2 decreases affinity of C13.28 for GRK2 in the flow cytometry RNA-protein binding assay. IC50 ± SEM values for wild-type GRK2 and GRK2-FG-6A, measured as a function of decreased detection of F-GRK2 in complex with bead-bound C13.28, were 3.3 ± 0.3 and 510 ± 170 nM, respectively. A representative experiment is shown.