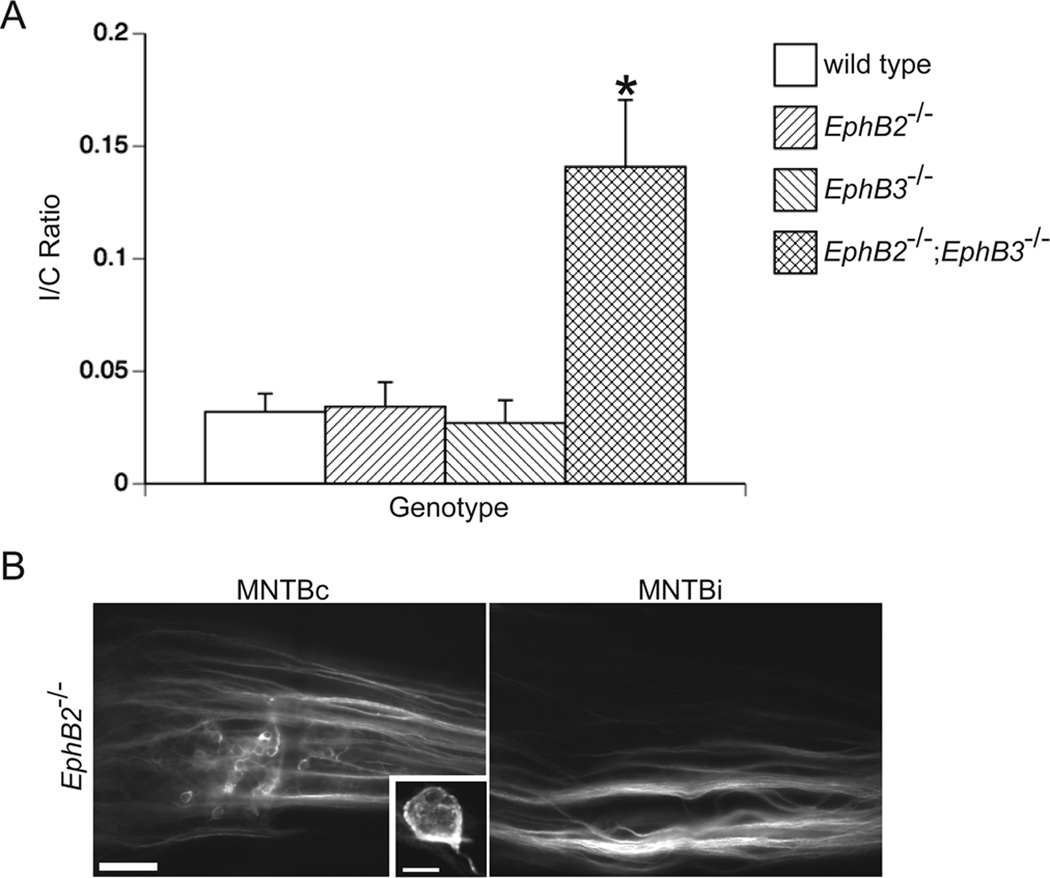
Figure 7.
EphB2 and EphB3 are necessary for the normal development of the VCN-MNTB projection. After dye placement into VCN on one side, labeled calyceal terminations were counted in the ipsilateral MNTB (MNTBi) and contralateral MNTB (MNTBc) to calculate an ipsilateral/contralateral (I/C) ratio in wild type, EphB2−/−, EphB3−/−, and EphB2−/−;EphB3−/− mice. Null mutations in EphB2 or EphB3 alone do not phenocopy EphB2;EphB3 double mutant mice, which have I/C ratios greater than wild type mice (A; P < 0.05, asterisk). Mean I/C ratios from EphB2 and EphB3 single mutant mice do not differ from the mean I/C ratio of wild type mice (A; P > 0.05). Projections from VCN are restricted to MNTBc in EphB2−/− mice, suggesting that ephrin-B reverse signaling is not elicited by EphB2 alone (B). A high-power image of a typical calyx of Held is shown in the inset of panel B. Scale bar in panel B represents 100 µm. Scale bar in the panel B inset represents 10 µm.