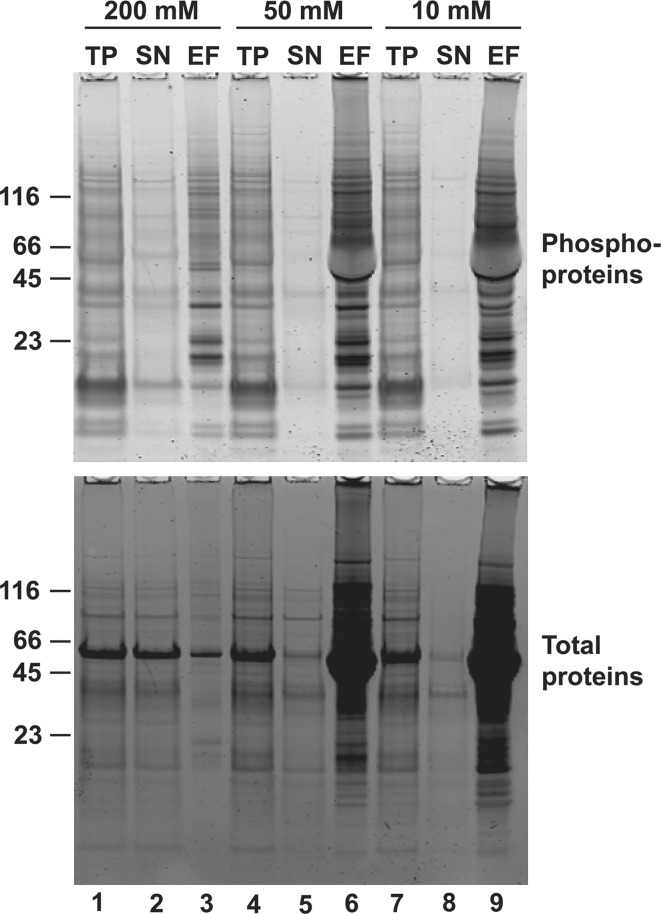
Fig. 5.
The dependence of the selectivity and sensitivity of Al(OH)3-MOAC on the concentration of acidic amino acid salts in incubation and washing buffers. The concentrations tested were 200, 50 and 10 mM for each acidic amino acid (glutamic acid and aspartic acid). Proteins (5 mg) in incubation buffer before (TP), and after incubation with the aluminum hydroxide matrix (SN) together with TCA precipitated candidate phosphoproteins from the eluted fraction (EF, corresponding to 0.5 mg of total proteins each lane) were analyzed by NuPAGE 4–12% Bis–Tris gels. Gels were stained with Pro-Q Diamond to detect phosphoproteins, and subsequently with SYPRO Ruby to visualize total proteins. The original 200 mM concentration showed high selectivity but quite low sensitivity since a number of phosphoproteins ended up in the flow-through. On the other hand, 50 and 10 mM concentrations showed high sensitivity since no phosphoproteins remained in the flow-through, but the selectivity was too low because almost all the proteins (not only the phosphoproteins) appeared in the eluate. (Röhrig et al. 2008. Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA. Reproduced with permission.)