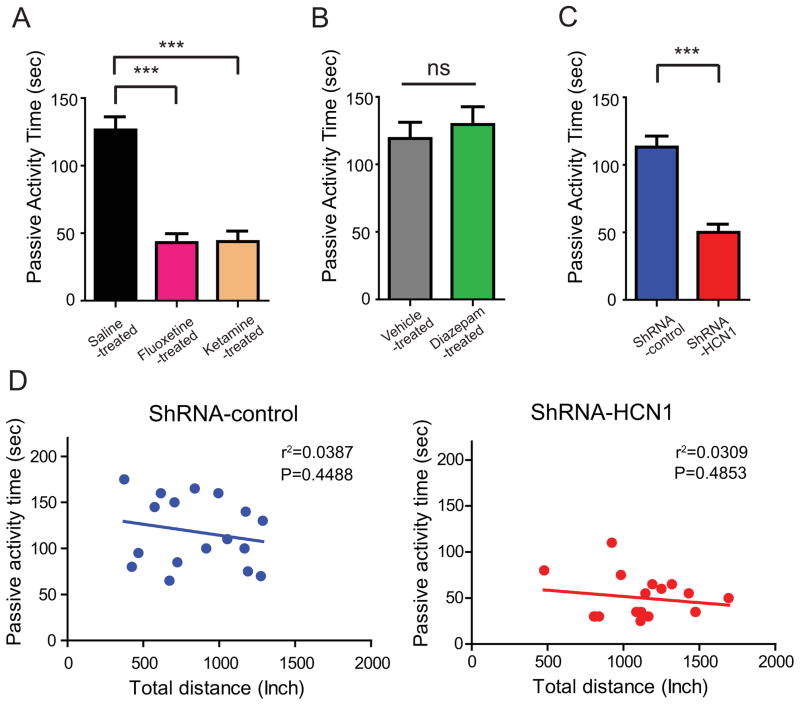
Figure 6. Knockdown of HCN1 by lentiviral-shRNA-HCN1 in the CA1 region of the dorsal hippocampus promoted antidepressant-like effects in the forced swim test.
(A) 10- to 12-week-old rats were treated with saline i.p. (n=17), 10 mg/kg fluoxetine i.p. (n=13), or 15 mg/kg ketamine i.p. (n=13) 30 min before the forced swim test as a positive control. Rats treated with fluoxetine or ketamine displayed significantly less passive activity time compared to rats treated with saline. (B) Diazepam-treated rats (1mg/kg i.p. n=12) had no effect on the forced swim test compared to vehicle-treated rats (n=13). (C) ShRNA-HCN1-infected rats (n=18) displayed significantly less passive activity time compared to shRNA-control-infected rats (n=17). Behavior despair as indicated by passive activity time was determined in the last 4 min of the forced swim test. (D) There was no significant correlation between the passive activity time (sec) in the forced swim test and the total distance (inch) in the open field test analyzed with linear regression. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001.