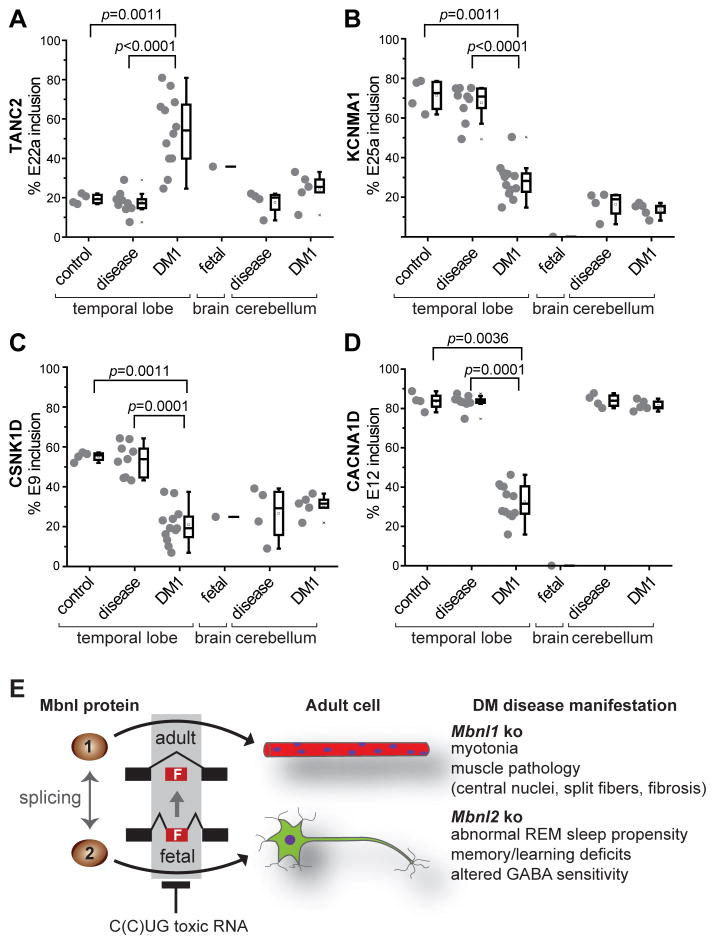
Figure 7. MBNL2 Brain RNA Splicing Targets Are Dysregulated in DM1.
(A–D) Analysis of DM1 brain for splicing perturbations predicted from the Mbnl2 mouse knockout model. RT-PCR splicing analysis of TANC2, KCNMA1, CSNK1D and CACNA1D using RNAs isolated from normal control temporal cortex (control, n = 4), disease control temporal cortex (disease, n = 9), DM1 temporal cortex (DM1, n=12), fetal control whole brain (fetal, n=1), disease control cerebellum (disease, n=4) and DM1 cerebellum (DM1, n=5) by RT-PCR.
(E) MBNL loss-of-function model for myotonic dystrophy. MBNL1 and MBNL2 function as alternative splicing factors during postnatal development of muscle (red myofibers with blue myonuclei) and brain (green neuron), respectively. Note that MBNL1 and MBNL2 cross-regulate the alternative splicing of key MBNL exons, including a 54 nt exon (MBNL1 exon 7, MBNL2 exon 6) which includes a nuclear localization sequence (Figure S7), so loss of MBNL2 could lead to an increase in nuclear levels MBNL1 and partial restoration of adult splicing patterns since both proteins recognize a YGCY motif.