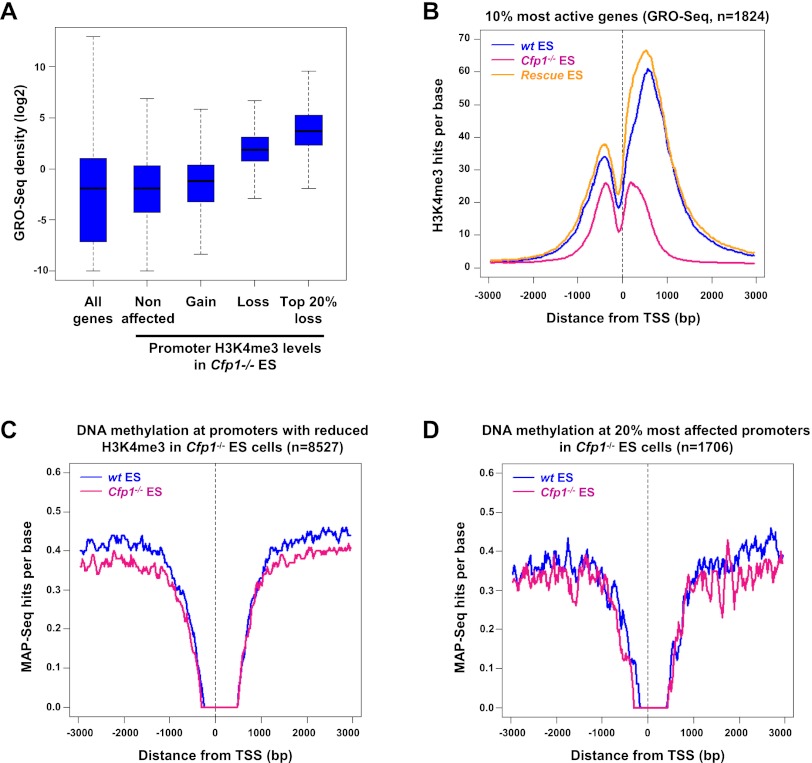
Figure 2.
Cfp1 deficiency preferentially affects H3K4me3 at highly expressed genes without altering their DNA methylation. (A) GRO-seq density distribution in wild-type (wt) ES cells for all Ensembl genes (All genes); for genes whose H3K4me3 is not affected (Nonaffected, n = 8663), increased (Gain, n = 1799), or decreased (Loss, n = 8527); or for the 20% most affected (Top 20% loss, n = 1706) in Cfp1−/− ES cells. Box plots represent the central 50% of the data (filled box), the median value (central bisecting line), and 1.5× the interquartile range (whiskers). (B) Composite profile showing H3K4me3 signal for wild-type (blue), Cfp1−/− (pink), and wild-type rescue (orange) ES cells for the 10% most active of all H3K4me3-positive Ensembl genes in wild-type ES cells, as judged by GRO-seq read density (n = 1824). (C) Composite profile showing MAP-seq signal for wild-type (blue) and Cfp1−/− (pink) ES cells at 8527 Ensembl promoters showing decreased H3K4me3 in Cfp1−/− ES cells. MAP-seq identifies clusters of methylated CpGs using biochemical affinity for an immobilized methyl-CpG-binding domain (MBD). (D) The same as C but representing only the 20% most affected promoters with respect to H3K4me3 loss in Cfp1−/− ES cells (n = 1706).