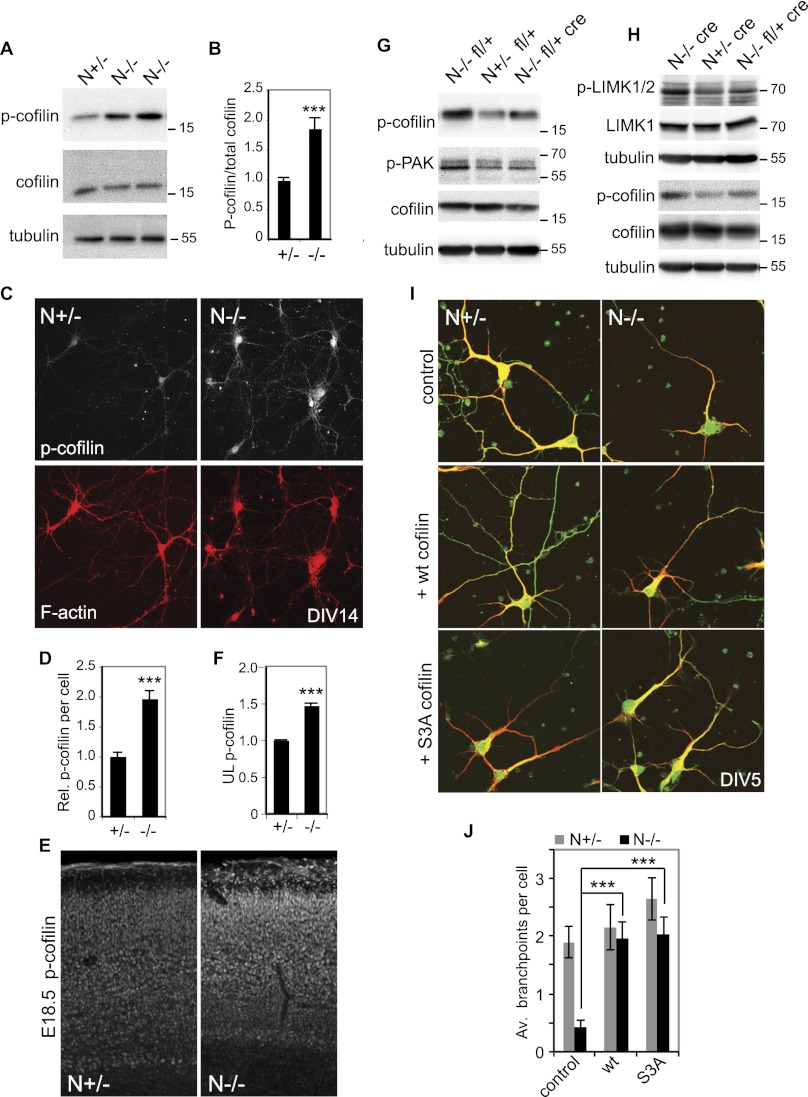
Figure 6.
Cofilin is regulated by NOMA-GAP during cortical development. (A,B) Loss of NOMA-GAP leads to an increase in cortical cofilin phosphorylation at Ser 3. (A) Total and phospho-Ser 3 cofilin levels were detected by Western blot of E17.5 cortical lysates derived from littermate embryos. (B) Quantification of specific phospho-Ser 3 cofilin levels from Western blot analysis. Phospho-cofilin/total cofilin values were calculated relative to the average value for N+/− littermate controls. The change in specific cofilin phosphorylation was then compared across different litters. n = 14 +/− and 16 −/− animals; P = 1.4 × 10−4. (C,D) Elevation of phospho-Ser 3 cofilin levels in N−/− cortical cells. (C) Cortical cells derived from littermate E16.5 embryos were cultured for 14 d and stained in parallel for phospho-cofilin (white) and F-actin (red). (D) Quantification of the average relative levels of phospho-Ser cofilin in the soma of N+/− and N−/− DIV14 cortical cells. n = 35 +/− and 31 −/− cells. P = 6.6 × 10−9. (E,F) Phospho-Ser 3 cofilin levels are increased in the neocortex of N−/− mice. (E) Fifty-micrometer vibratome coronal brain sections of littermate E18.5 embryos were stained in parallel for phospho-Ser 3 cofilin. (F) Quantification of phospho-Ser 3 cofilin in the upper cortical layer of E18.5 animals. The relative mean staining intensity in the upper cortical layers of three pairs of littermate heterozygote and mutant embryos is shown. P = 7.7 × 10−5. (G,H) Cortical cofilin, PAK, and LIMK phosphorylation are regulated by Cdc42 downstream from NOMA-GAP. Representative Western blots of cortical lysates derived from littermate E17.5 embryos were blotted for phospho-Ser 3 cofilin (p-cofilin), phospho-PAK (p-PAK), and/or phospho-LIMK (p-LIMK1/2) and LIMK1 as indicated. Detection of phospho and total forms of cofilin and LIMK were carried out on duplicate Western blots. The tubulin loading controls shown were carried out on the membranes with anti-phospho antibodies. (I,J) Expression of cofilin promotes dendritic branching in N−/− cortical cells. (I) E16.5 primary cortical cells were transfected 1 d after plating with empty vector (control), wild-type cofilin, or S3A cofilin-expressing constructs together with a myr-GFP-expressing construct. Samples were stained at DIV5 for MAP2 (red) and GFP (green). (J) Quantification of the number of branchpoints per cell. n = 30, 32, 32, 38, 34, and 35 cells for the conditions from left to right. PANOVA = 4.2 × 10−5; PN−/− control vs. wt cofilin = 7.9 × 10−5; PN−/− control vs. SA = 7.7 × 10−6; PN+/− control vs. wild-type cofilin = 0.6.