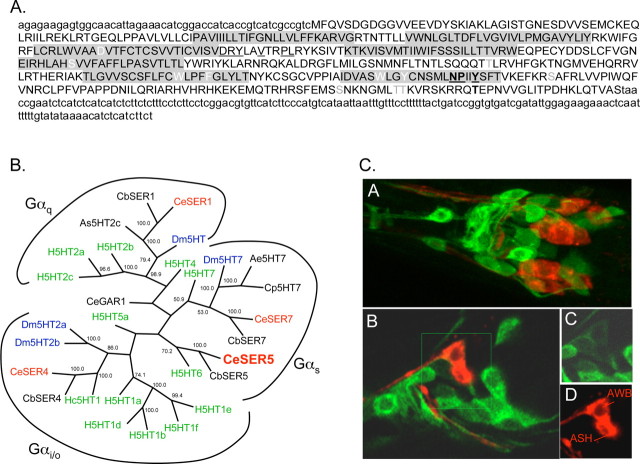
Figure 5.
SER-5 is most identical to invertebrate/mammalian 5-HT receptors and is expressed in both neurons and muscle. A, Predicted amino acid sequence of SER-5. The full-length ser-5 cDNA sequence was generated by 5′ and 3′ RACE as described in Materials and Methods. Putative transmembrane regions are shaded in gray. Residues potentially involved in BA binding are in white, and G-protein-coupling residues are underlined (Strader et al., 1989; Choudhary et al., 1993; Moro et al., 1993; Barak et al., 1994; Almaula et al., 1996; Roth et al., 1997). Potential PKA and PKC phosphorylation sites were identified using ScanProsite, and are indicated in bold and gray, respectively (Gattiker et al., 2002). Sequestration and desensitization sites are bold and underlined (Barak et al., 1994). B, Unrooted phylogenetic tree of vertebrate and invertebrate 5-HT receptors. Sequences were modified to remove hypervariable regions by the deletion of the N termini 3 aa before the first predicted transmembrane domains, the third intracellular loops, 8 aa after and 6 aa before predicted transmembrane domains 5 and 6, respectively, and the C termini, 12 aa after predicted transmembrane domain 7. Annotated sequences were initially aligned using MegAlign in DNAStar with ClustalW, and using parameters defined in Materials and Methods and fine-tuned by hand. Bootstrapping was undertaken in DNAStar (1000 replicates with random seed). Homo sapiens (H) in green: H5HT1a (CAA40962), H5HT1b (P28222), H5HT1d (P28221), H5HT1e (CAA77558), H5HT1f (AAA36605), H5HT2a (CAA40963), H5HT2b (CAA54513), H5HT2c (AAF35842), H5HT4 (Q13639), H5HT5a (CAA57168), H5HT6 (AAA92622), Hs5HT7 (CAH69965), Caenorhabditis elegans (Ce) in red: CeSER1 (NP_001024728), CeSER4 (NP_497452), CeSER7 (NP_741730), CeSER5. [SER-5 is a potentially new 5-HT receptor in C. elegans, based on new sequence information on ser-5 (based on 5′ and 3′ RACE) (Hapiak et al., 2009) and also based on two 5-HT-dependent behavioral phenotypes, egg laying and octanol avoidance (Hapiak et al., 2009; Harris et al., 2009).] Caenorhabditis briggsae (Cb): CbSER-1 (CAE69959), CbSER4 (CAE69091), CbSER7 (CAE58847), CbSER5 (CAE60436), Aedes egyptii (Ae): Ae5HT7 (AAG49292), Drosophila melanogaster (Dm) in blue: Dm5HT7, (Dm5HT2a, NP_725849, NP_524599), Dm5HT2a (NP_725849), Dm5HT2b (CAA77571), Dm5HT (NP_730859), Hemonchus contortus (Hc): Hc5HT1e (AAO45883), Ascaris suum (As): As5HT-2c (AAC78396). C, GFP fluorescence from a full-length ser-5p::ser-5::gfp transgene that includes sequence coding for GFP inserted into the predicted C terminus of the receptor. CA, Merge of GFP fluorescence and 1,1′-dioctadecyl-3,3,3′,3′-tetramethylindodicarbocyanine perchlorate (DiD, a lipophilic dye) staining in the nerve ring. CB, Single Z-section of GFP/DiD merge in the nerve ring. CC, CD, Insets from CB with GFP fluorescence (CC) and DiD staining (CD).