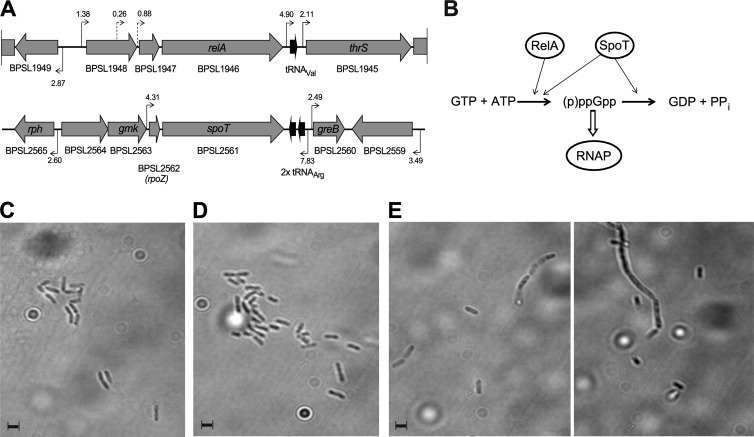
Fig 1.
Genetic organization and enzymatic activities of RelA-SpoT family proteins in B. pseudomallei and cell morphology of RelA-SpoT family mutants. (A) Schematic overview of the chromosomal regions surrounding the relA gene (BPSL1946 [top]) and the spoT gene (BPSL2561 [bottom]). Predicted promoters and their linear discriminant function (LDF) score are indicated. (B) Schematic of the classical synthesis pathway of (p)ppGpp. pppGpp is produced from GTP and ATP by either RelA- or SpoT-dependent mechanisms and is subsequently converted to ppGpp. ppGpp interacts directly with the RNA polymerase enzyme (RNAP) and thus affects gene expression. The effects of ppGpp induction are relieved by SpoT-mediated hydrolysis of ppGpp. (C to E) Cell morphology of B. pseudomallei wild-type strain K96243 (C), a K96243 ΔrelA single mutant (D), and a K96243 ΔrelA ΔspoT double mutant (E). All strains were grown to early stationary growth phase (24-h incubation at 37°C) in LB broth, and bacterial cells were visualized by bright-field microscopy at a magnification of ×100. The scale bars represent the average length of K96243 wild-type cells. In panel E, two images of K96243 ΔrelA ΔspoT mutant cells are presented, one focused on single cells (left) and one focused on a filament (right).