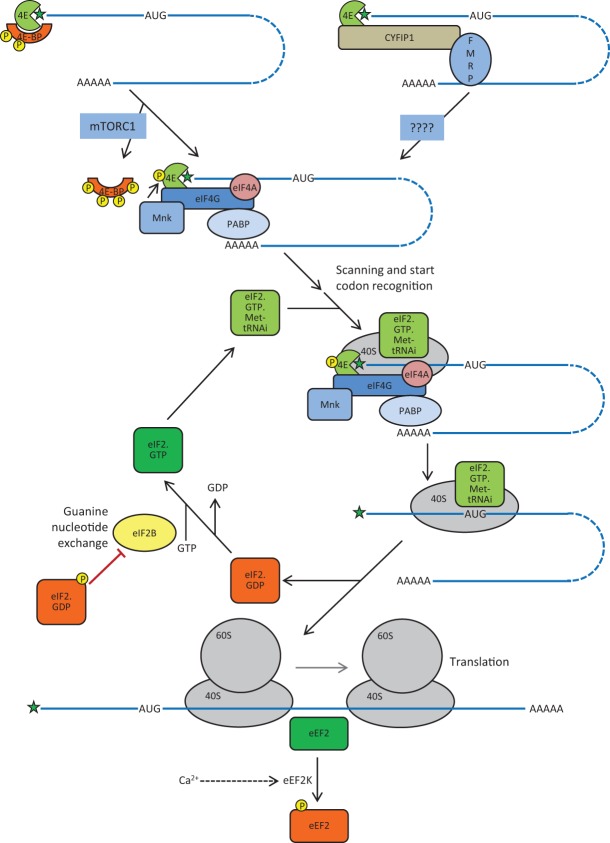
Figure 1.
Schematic depiction of the steps in mRNA translation that are discussed in the text, including the recruitment of eIF4E to the 5′-cap (star) of the mRNA (blue line). Phosphoryation events are indicated by “P” in a yellow circle. Following phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 by mTORC1, eIF4E is able to bind eIF4G and associated factors, leading to recruitment of the 40S ribosomal subunit and associated eIF2·GTP·Met-tRNAi to the mRNA. After scanning and location of the start codon, eIF2-bound GTP is hydrolyzed to GDP, the 60S subunit joins and elongation can commence. eIF2·GDP is recycled to eIF2·GTP by eIF2B. During elongation, eEF2 mediates movement (“translocation”) of the ribosome along the mRNA; phosphorylation of eEF2, catalyzed by the Ca2+-activated eEF2 kinase (eEF2K), inactivates it, slowing elongation.