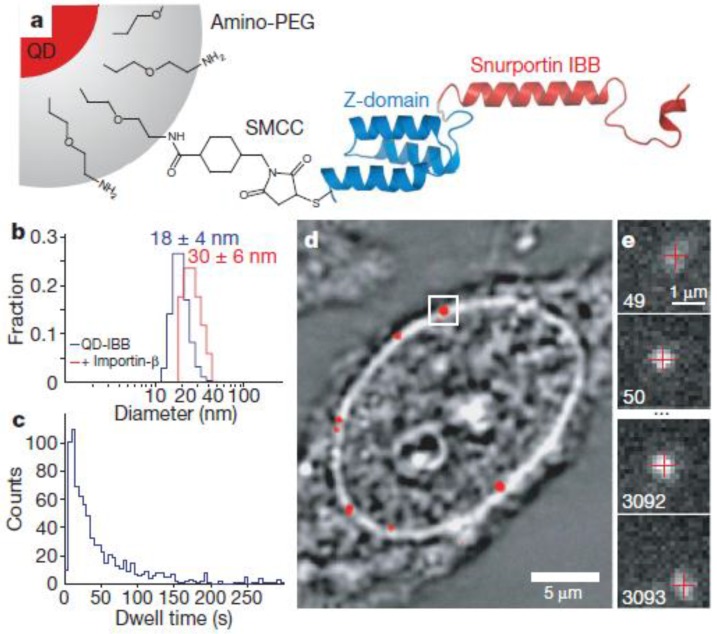
Figure 5.
Experimental design. (a) Diagram of a QD-based cargo. The snurportin-1 importin-β binding (IBB) /Z-domain fusion protein is coupled via a bifunctional succinimidyl-4-(N-maleimidomethyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylate crosslinker (SMCC) to the amino-PEG polymer coat of a fluorescent QD. The three helix Z-domain acts as a spacer to correctly present the importin-β binding for biological function. Not to scale. (b) Dynamic light scattering size distributions of QD- IBB cargos in the presence and absence of IBB. (c) Dwell time distribution of all QD interactions with the nuclear pore complex. The time axis is truncated at 300 s. (d) Bright-field image of a nucleus with a QD fluorescence image (with background subtraction applied) overlaid in red. A single QD cargo at the nuclear envelope is boxed. (e) Individual consecutive frames from a single-molecule experiment showing the arrival (first frame) from the cytoplasm and departure (final frame) of the cargo into the nucleus. The centroids determined from fitting of the PSF (point spread function) are overlaid as red crosses. Frame numbers are in the bottom left hand corner of each frame. Movies were captured at 40 Hz. Reprinted with permission from Alan R. Lowe, Jake J. Siegel, Petr Kalab, Merek Siu, Karsten Weis, and Jan T. Liphardt, Fig.1, Nature Vol 467, 600-603 (2010). Copyright (2010) Nature Publishing Group. http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v467/n7315/full/nature09285.html.