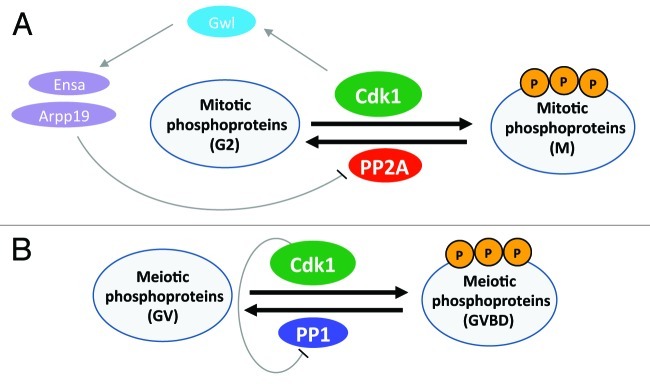
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the roles of Cdk1 during the G2-M transition in mitosis and in the germinal vesicle breakdown that occurs during resumption of meiosis. (A) Cdk1 kinase is activated and promotes the phosphorylation of mitotic phosphoproteins at the G2-M transition in mitosis. In order to maintain the phosphorylation status of the Cdk1 substrates, PP2A is inactivated by activation of Gwl by Cdk1. Active Gwl inhibits PP2A through the activation of Arpp19 and Ensa. (B) During the resumption of meiosis in oocytes, Cdk1 is activated and promotes the phosphorylation of meiotic phosphoproteins. Maintenance of the phosphorylation status of the meiotic phosphoproteins is ensured by phosphorylation and inhibition of PP1 by Cdk1. P, phosphorylation; Arpp19, cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein 19; Ensa, α-endosulfine.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.