Fig. 2.
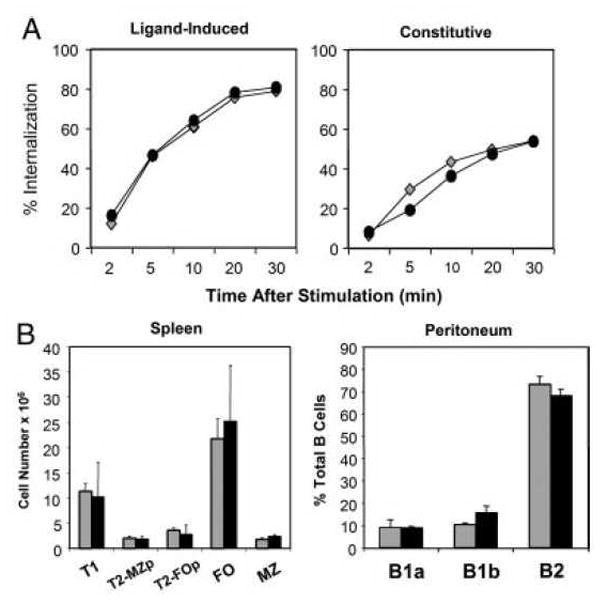
Early BCR-dependent signaling and B cell development are normal in gp91phox KO mice. (A) BCR internalization was analyzed using flow cytometry. To examine BCR internalization, WT (diamonds) or gp91phox KO (circles) B cells were incubated with F(ab′)2 anti-IgM to analyze ligand-induced internalization; or Fab anti-IgM to measure constitutive internalization. Data are representative of three experiments. (B) Splenic B subsets cells were analyzed as follows: Follicular (FO) B cells: IgMintIgDhiCD21lo; Transitional 1 (T1): IgDloIgMhiCD21lo. Transitional 2 Follicular Precursor (T2-FOp): IgDhiIgMhiCD21lo. Transitional 2 MZ precursor (T2-MZp): IgDhiIgMhiCD21hi. Marginal Zone (MZ): IgDloIgMhiCD21hi. WT (grey bars) and gp91phox KO (black bars). Peritoneal B cell subsets were analyzed using CD11b, CD5 and IgM as markers. B1a cells: CD11bhi, IgMlo, CD5hi. B1b cells: CD11bhi, IgMlo, CD5neg. B2: CD11bneg, IgMhi, CD5neg. Data mean + SD (n=3 spleens) and are representative of four independent experiments.
