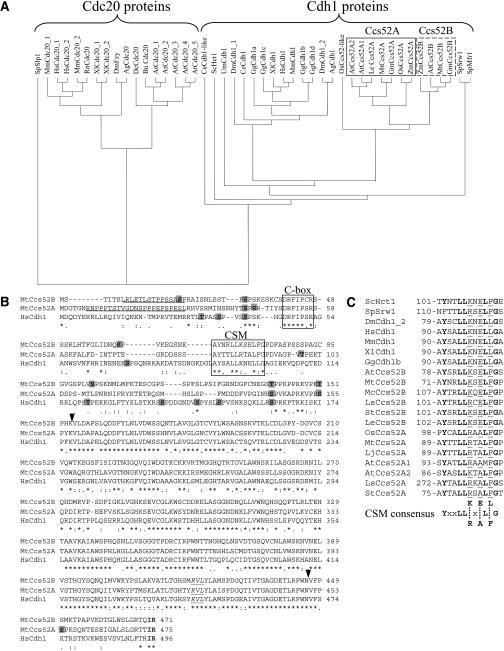
Figure 1.
The Structure and Conserved Motifs of the M. truncatula Ccs52A and Ccs52B Proteins and Their Relatedness to Other APC Activators.
(A) Phylogenetic tree of APC activators classifies the Cdc20 and Cdh1/Ccs52 proteins in separate groups. BLASTX and TBLASTX were performed with Mtccs52A and Mtccs52B cDNA. Translated sequences were aligned with CLUSTAL W at EMBL-EBI and visualized using the TreeView program.
(B) Comparison of MtCcs52A and MtCcs52B to the H. sapiens Cdh1 protein. Putative PEST motifs are underlined; S and T residues of potential CDK phosphorylation sites are indicated on shaded background; the conserved terminal IR residues are in bold; the C-box and CSM sequences are shown in frames; and the conserved cyclin binding RVL motif is in italic and underlined. Arrowheads indicate the start and the end of the WD40 repeat region.
(C) The CSM is conserved in the Cdh1 proteins. A consensus sequence is deduced, where identical residues are in bold and x indicates any amino acid. Positions of the CSMs are given. Ag, Anopheles gambiae; At, A. thaliana; Bn, Brassica napus; Ce, Caenorhabditis elegans; Dc, Daucus carota; Dm, D. melanogaster; Gg, Gallus gallus; Gm, G. max; Hs, H. sapiens; Le, Lycopersicon esculentum; Lj, Lotus japonicus; Ls, Lactuca sativa; Mc, Mesembryanthemum crystallinum; Mm, Mus musculus; Mt, M. truncatula; Os, Oryza sativa; Rn, Rattus norvegicus; Sc, S. cerevisiae; Sp, S. pombe; St, Solanum tuberosum; Um, Ustilago maydis; Xl, Xenopus laevis; Zm, Zea mays.