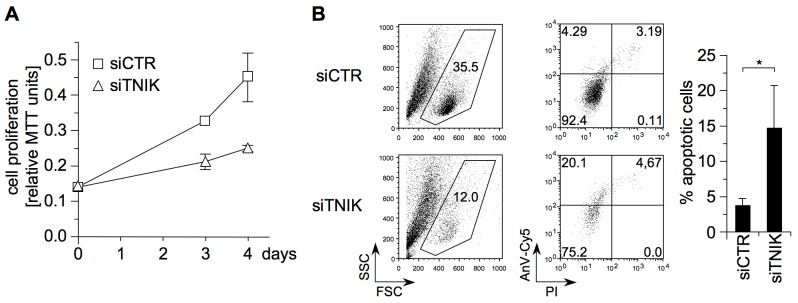
Figure 5. TNIK mediates proliferation and survival in EBV-transformed human B-cells.
(A) The knockdown of TNIK inhibits proliferation of LCLs. EREB2-5 cells were seeded in the presence of Accell siRNA targeting TNIK or non-targeting siRNA. Cell proliferation was monitored at the indicated times by MTT conversion. Shown are the results of one representative experiment in triplicates of three independent experiments. (B) Apoptosis induction by TNIK knockdown in LCLs. EREB2-5 cells were incubated with Accell siTNIK or siCTR, as indicated. Apoptosis was monitored after 3 d in the presence of siRNA by co-staining of the cells with Cy5-labeled annexin V (AnV-Cy5) and propidium iodide (PI). The population of intact cells within the lymphocyte gate in the forward scatter (FSC)/sideward scatter (SSC) plot (left panels) was strongly reduced after the knockdown of TNIK. The gated cells were then analyzed for apoptosis rates, indicated by PI−/AnV-Cy5+ staining (right panels). The graph shows mean values of PI−/AnV-Cy5+ percentages of three independent experiments ± standard deviations; two-tailed Student's t test. *p = 0.033.