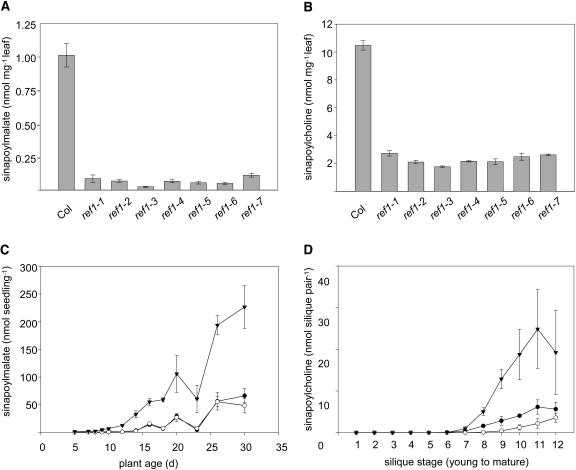
Figure 2.
Impact of the ref1 Mutation on Sinapate Ester Content.
(A) Sinapoylmalate content of leaves of 3-week-old wild-type plants and each of the seven ref1 mutants. Data represent the mean of at least four samples ±1 sd. Col, wild-type Columbia ecotype.
(B) Sinapoylcholine content of seeds of the same series of plants as in (A). Data represent the mean of at least four samples ±1 sd.
(C) Sinapoylmalate content of entire rosettes from wild-type (inverted triangles), ref1-1 (closed circles), and ref1-2 (open circles) plants sampled throughout plant development. Data represent the mean of at least four samples ±1 sd.
(D) Sinapoylcholine content of developing siliques from wild-type (inverted triangles), ref1-1 (closed circles), and ref1-2 (open circles) plants. Siliques from individual inflorescences were harvested in pairs from top to bottom when the bottom silique turned yellow. Data represent the mean of at least four samples ±1 sd.