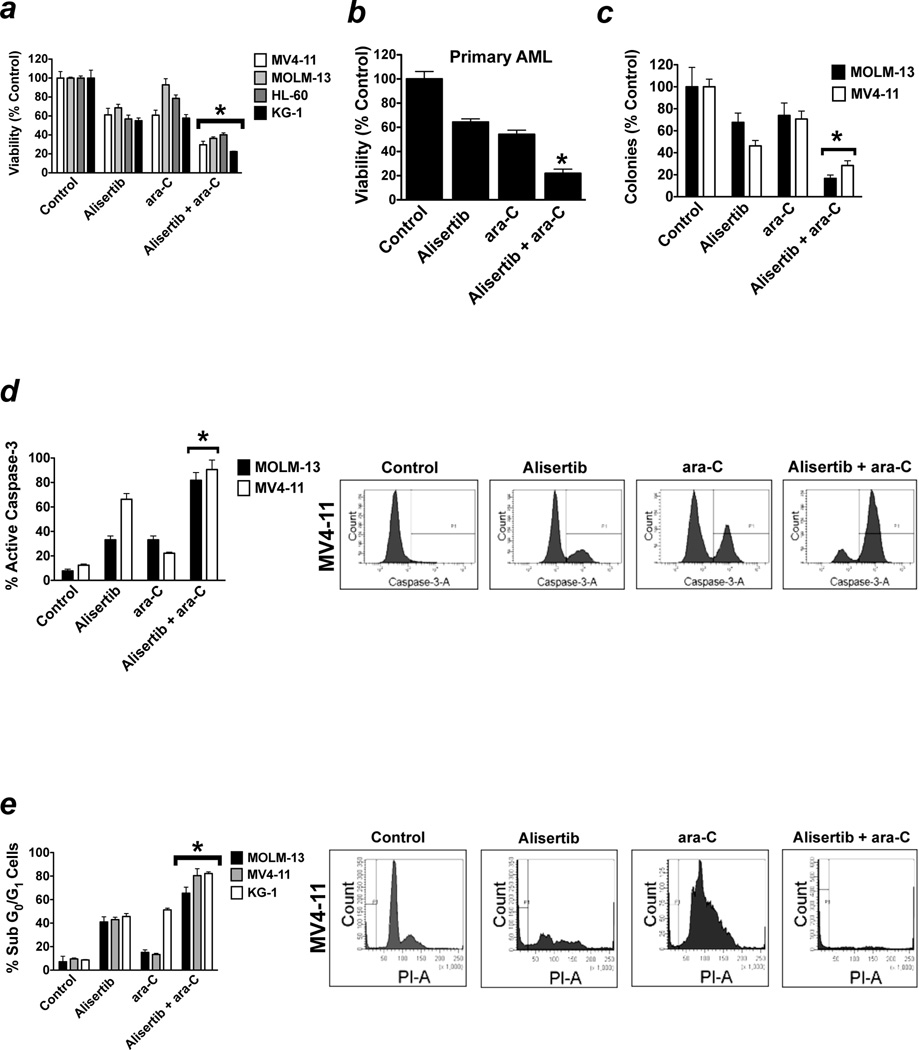
Figure 4. Alisertib significantly increases the efficacy of ara-C.
(a–b) MLN8237 potentiates the anti-leukemic effects of ara-C. Human AML cell lines (MV4-11, MOLM-13, Hl-60, and KG-1, panel a) and primary AML cells (panel b) were treated with 100 nM alisertib, 100 nM ara-C, or the combination for 72 hours. Percentages of viable cells were determined by MTT assay. n = 3 ± SD, (*p ≤ 0.05, combination drug treatment vs. single agent drug treatments). (c) The combination of alisertib and ara-C cooperate to disrupt clonogenic survival. MOLM-13 and MV4-11 cells were treated 100 nM alisertib, 100 nM ara-C, or both for 24 hours. Drugs were washed away and cells were plated in Methocult. Colonies were scored on day 14. n = 3 ± SD, (*p ≤ 0.05, combination drug treatment vs. single agent drug treatments). (d–e) Alisertib augments ara-C-mediated apoptosis. Cells were treated with 100 nM alisertib, 100 nM ara-C, or both drugs for 48 hours. Drug-induced apoptosis was quantified by active caspase-3 staining (d) and PI/FACS (e). Representative histograms generated from experiments conducted with MV4-11 cells are shown. n = 3 ± SD, (*p ≤ 0.05, combination drug treatment vs. single agent drug treatments).