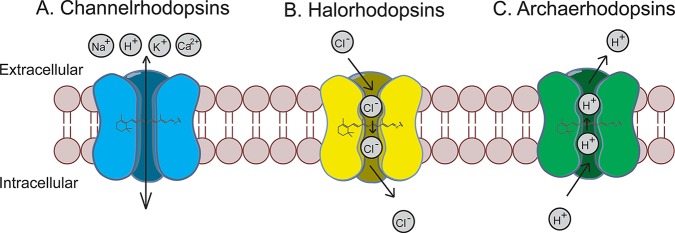
Figure 1.
Optogenetic molecular sensors. Upon light illumination, channelrhodopsins passively transport Na+, K+, H+, Ca2+ down their electrochemical gradients to depolarize neurons (A); halorhodopsins actively pump Cl– into the cell to hyperpolarize neurons (B); archaerhodopsins actively pump H+ out of the cell to hyperpolarize neurons (C).