Figure 2.
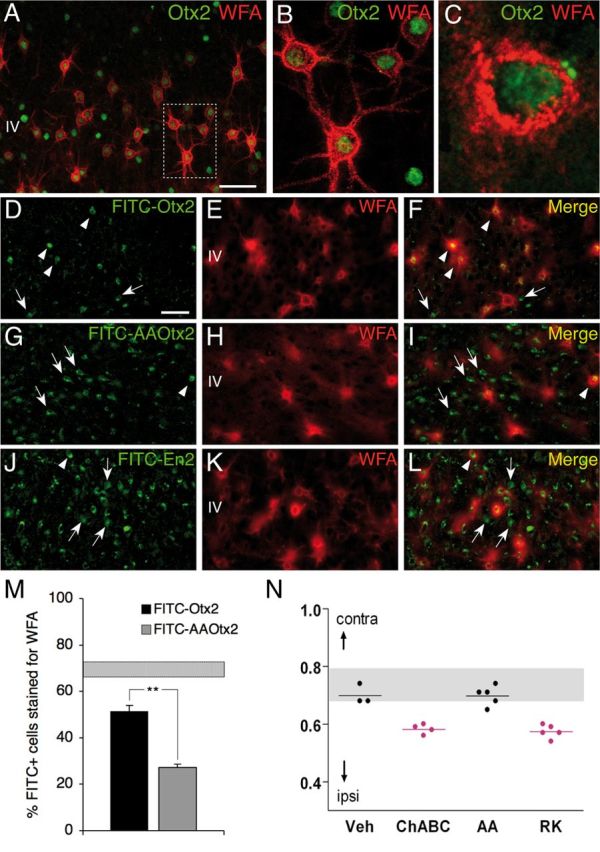
Preferential Otx2 capture by PV cells requires the RK doublet. A–C, Codetection of WFA and Otx2 in layer IV of P60 mouse V1b. Inset in A is magnified in B. C, Staining performed under nonpermeabilizing conditions reveals extracellular/membranous Otx2 staining. D, G, J, Distribution of FITC-labeled Otx2 (D), AA-Otx2 (G), and En2-FITC (J) recombinant proteins after injection into P60 mice. E, F, H, I, K, L, WFA detection (E, H, K) and merged FITC-Otx2 images reveal preferential Otx2 capture by WFA-labeled cells (F) compared with AA-Otx2 (I) and En2 (L). Arrowheads, Double-stained cells; arrows, FITC-positive cells not stained with WFA. Scale bars: A, 50 μm; (in D) D–L, 50 μm. M, Percentage of FITC-positive cells costained for WFA after FITC-Otx2 or AA-Otx2 injection. Striped bar, endogenous percentage of Otx2-positive cells costained for WFA (mean ± SEM). N, CBI of single-unit recordings from mice treated with ChABC, RK, or AA peptide after a period of brief MD (4 d) in adulthood. Both ChABC and RK peptide infusion similarly reactivate visual cortical plasticity (decrease of CBI compared with non-MD), which is not typically seen in saline- or AA peptide-infused adult mice.
