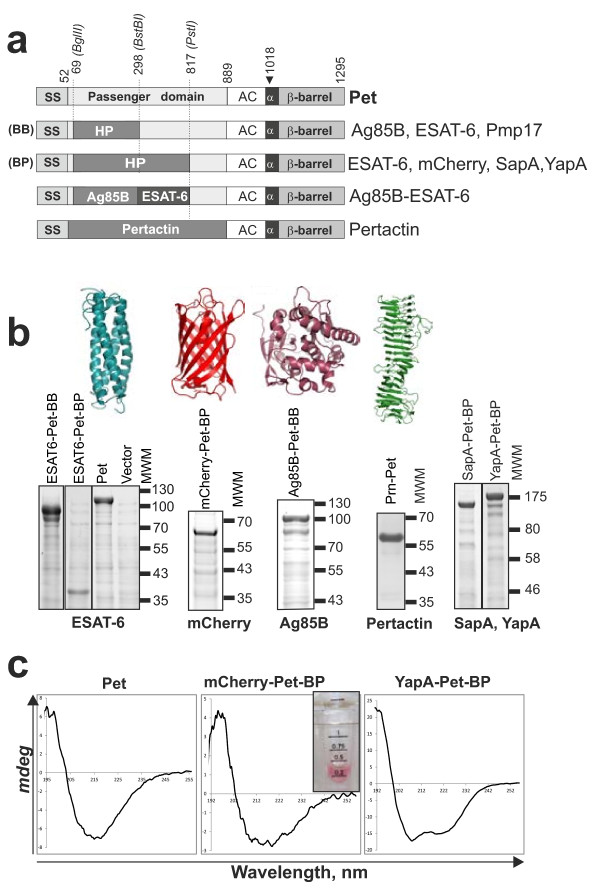
Figure 1.
AT-mediated accumulation of heterologous proteins in the culture medium. (A) Schematic diagram of Pet fusion constructs. Heterologous protein insertions in the Pet passenger domain are shown by dark boxes marked HP or with the name of the protein, and are also listed on the right. Abbreviations BB and BP on the left refer to the type of protein fusion generated by insertion of foreign DNA into the pet gene between the restriction sites BglII and BstBI or BglII and PstI, respectively. The co-ordinates above the figure are given for the amino acids derived from the de novo synthesised pet gene. The positions of these sites in the context of the quaternary structure are depicted in Additional file 1: Figure S1. The arrow at position 1018 denotes the cleavage site in the α-helix that effects release of the passenger domain into the culture medium. Modification of this site results in surface display of molecules (Figure 2). The abbreviations SS, AC and α denote the positions of the signal sequence, autochaperone domain and α-helix, respectively. (B) The presence of secreted heterologous proteins in the culture medium was detected by SDS-PAGE or immunoblotting with anti-Pet. Equivalent volumes of medium were analysed. The structures of several heterologous proteins are depicted (not to scale). (C) Investigation of the folded state of secreted heterologous fusion proteins. Far-UV CD spectra of Pet and several heterologous proteins are shown in millidegrees (mdeg). mCherry-Pet-BP harvested from the culture supernatant is shown.