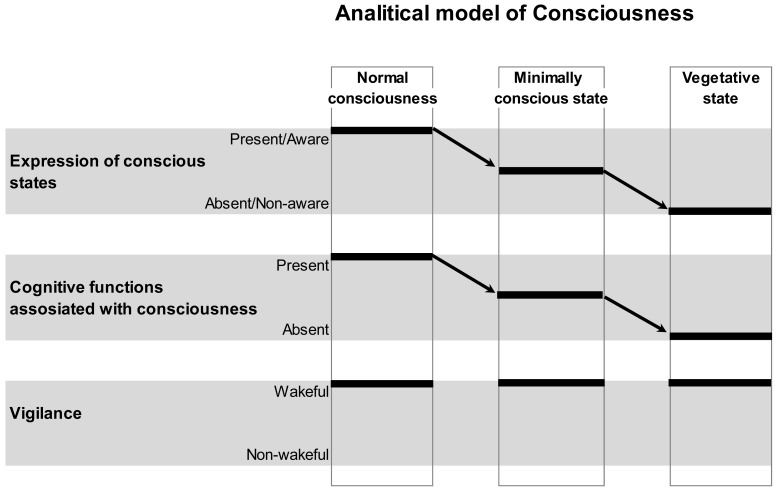
Fig. (1).
Schematic Illustration of the Analytical Model of Consciousness. On the horizontal plane, conscious states and related with them cognitive functions, as well as vigilance states are plotted. On the vertical plane, normal conscious state, minimally conscious state and unconscious (vegetative) state conditions are presented. Arrows indicate a decrease in the expression of conscious states and related with them cognitive functions from normal, to minimal and to unconscious conditions. Vigilance is supposed to be nearly identical in all three conditions. Therefore, within this analytical model, conscious expression could be reliably dissociated from the vigilance. However, it is clear from the graph that the expression of consciousness and the related with it conscious cognitive functions/operations could not be disentangled. This is a limitation of such a model. Figure is modified from [41].