Figure 1.
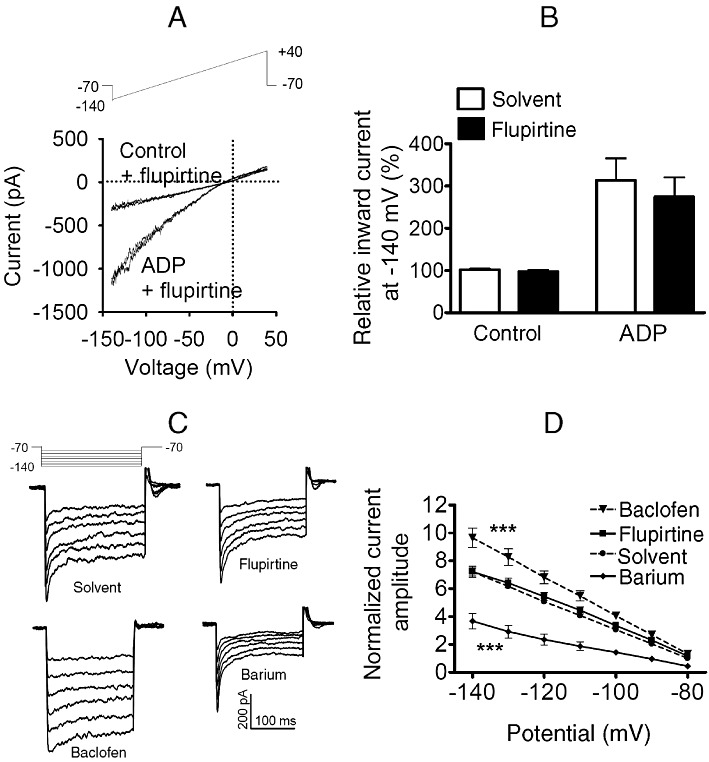
Effects of flupirtine on recombinant and native G-protein coupled inwardly rectifying K channels. (A, B) KIR3.1/3.2 concatemers and P2Y12 receptors were co-expressed in tsA cells. Currents were evoked by ramp depolarizations from −140 to 40 mV during periods of 200 ms. (A) Representative traces of recordings in the absence (control) or presence of ADP 100 µM, either with solvent or with 30 µM flupirtine. (B) Amplitudes of inward currents were determined at −140 mV; normalized amplitudes of currents obtained either in solvent or in 30 µM flupirtine, either alone (control) or together with 100 µM ADP, are shown (n = 7). (C, D) Currents were evoked in hippocampal neurons by 200 ms hyperpolarizations from a holding potential of −70 mV to potentials ranging from −80 to −140 mV with 10 mV increments as published previously (Jakob and Krieglstein, 1997). This pulse protocol was applied in the presence of either solvent or 100 µM baclofen, 10 µM flupirtine and 1 mM BaCl2, respectively. (C) Representative original traces. (D) Summary of results obtained in nine different neurons; for each neuron, all amplitude values were normalized to the amplitude determined in the presence of solvent at a potential of −80 mV. *** indicates statistically significant differences versus currents in the presence of solvent at P < 0.001 as determined by a two way ANOVA.
