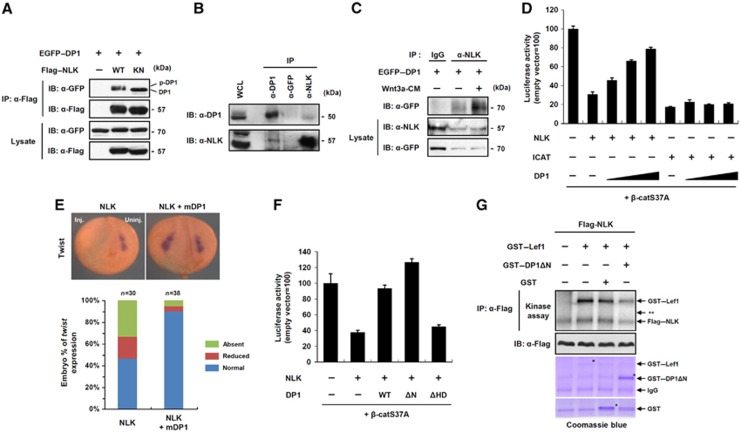
Figure 3.
Nuclear DP1 antagonizes kinase activity of NLK thereby enhancing Wnt/β-catenin signalling. (A) Cells were transfected with EGFP–DP1 and co-transfected with either Flag–NLK WT or kinase-inactive mutant (KN). IP and immunoblotting were performed with indicated antibodies. DP1 and phospho-DP1 bands are indicated. (B) Endogenous interaction of DP1 with NLK. (C) Cells expressing EGFP–DP1 were stimulated with either control-CM (marked as —) or Wnt3a-CM for 6 h. IP was performed with anti-NLK antibody or IgG. (D) TOP-FLASH activities were measured from cells transfected with indicated plasmids. Data represent average values from one representative experiment performed in triplicate. Error bars indicate standard deviations of triplicate. (E) mRNAs for NLK (4 ng), mDP1 (1 ng) and β-galactosidase (200 pg), a lineage tracer, were unilaterally injected. Inj.: injected side; Uninj.: uninjected side. At neurula stage, embryos were subjected to in situ hybridization for Twist. (F) TOP-FLASH activities were measured in cells transfected with indicated plasmids. Data represent average values from one representative experiment performed in triplicate. Error bars indicate standard deviations of triplicate. (G) In-vitro kinase assay of immunoprecipitated Flag–NLK toward purified GST-fusion proteins in the presence of 10μCi of [γ32-ATP]. ** indicates the expected size of DP1Δ N.