Figure 1.
BRDT Inhibition by the BET Bromodomain Inhibitor JQ1
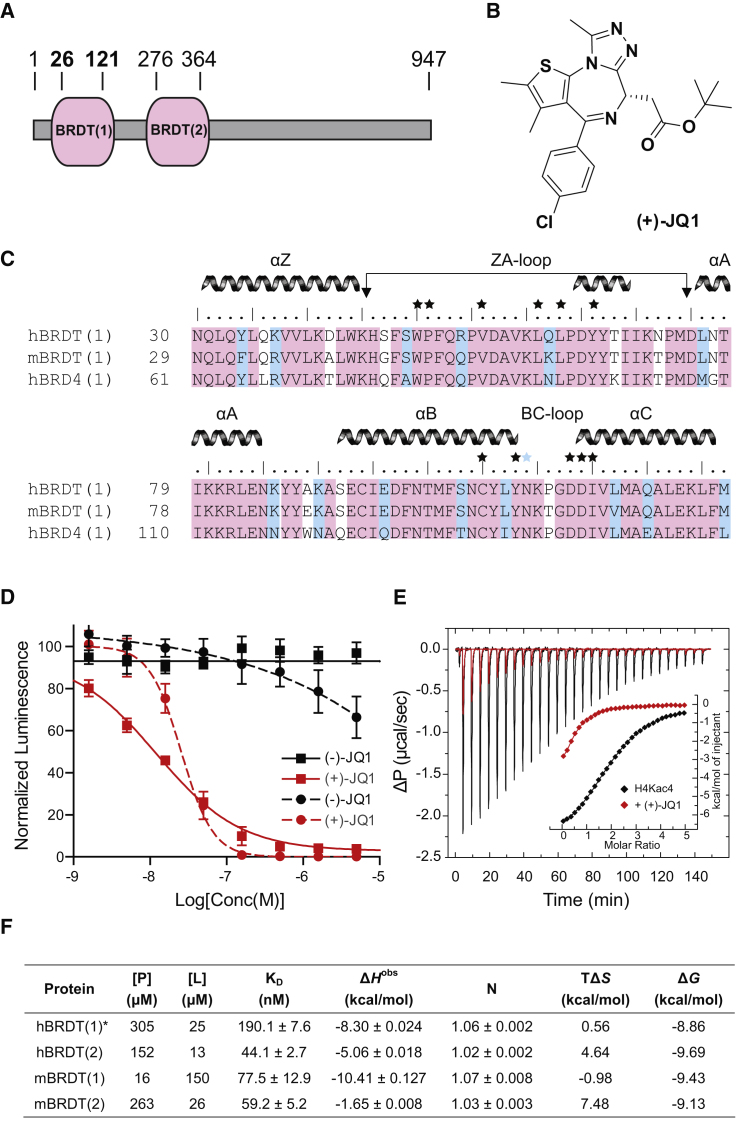
(A) Domain diagram of BRDT. Sequence boundaries for recombinant BRDT(1) are shown in bold.
(B) Structure of the active (+)-JQ1 enantiomer.
(C) Protein alignment reveals high sequence identity between homologous and orthologous domains. Identical (pink) and similar (blue) residues are highlighted. Major helical elements are depicted above the sequence. The conserved asparagine mediating acetyl-lysine recognition is depicted with a blue star. Contacts between (+)-JQ1 and BRDT(1) are depicted with a black star.
(D) Competitive inhibition of human (squares) and mouse (circles) BRDT(1) binding to synthetic biotinylated H4Kac4 by (+)-JQ1 using proximity detection assays (hBRDT(1) IC50 = 11 nM; mBrdt(1) IC50 = 10 nM).
(E) ITC data for titration of H4Kac4 into hBRDT(1) (black line) or into a 1:0.8 molar mixture of hBRDT(1) and (+)-JQ1 (red line). The inset shows normalized binding enthalpies corrected for heat of dilution as a function of binding site saturation. Solid lines represent a nonlinear least-squares fit using a single-site binding model.
(F) Equilibrium binding constants and binding energies of (+)-JQ1 to human and mouse BRDT bromodomains measured by ITC.