Figure 1.
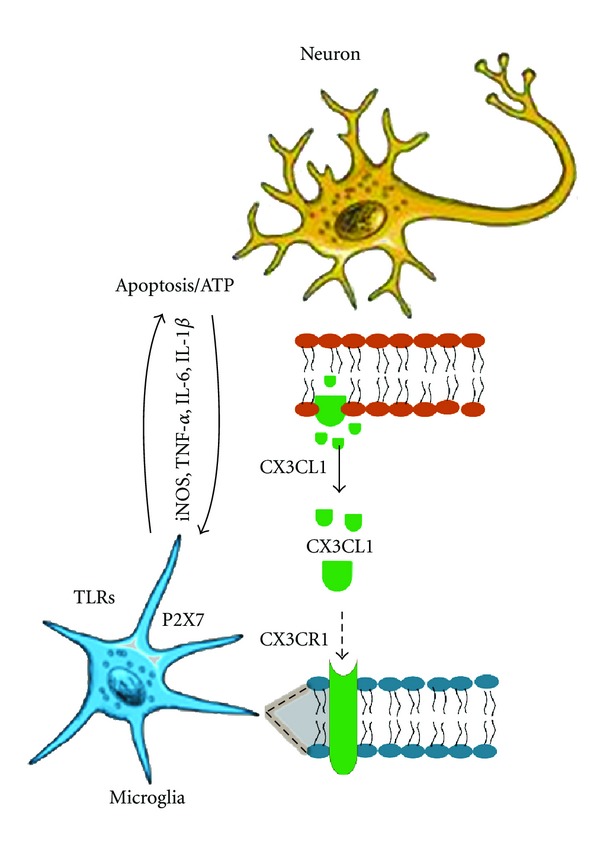
Initiation of inflammatory response following intraneuronal protein accumulation. Intraneuronal accumulation of pathogenic proteins causes ATP release by apoptotic neurons to activate purinergic microglia P2X7 receptors or TLRs. Activated microglia release proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-16, IL-1) and iNOS to activate astrocytes (via MCP-1 chemotaxis) and increase apoptosis in stressed neurons. To initiate a neuroprotective immune response, injured neurons may communicate via fractalkine (CX3CR1) and suppress inflammation.
