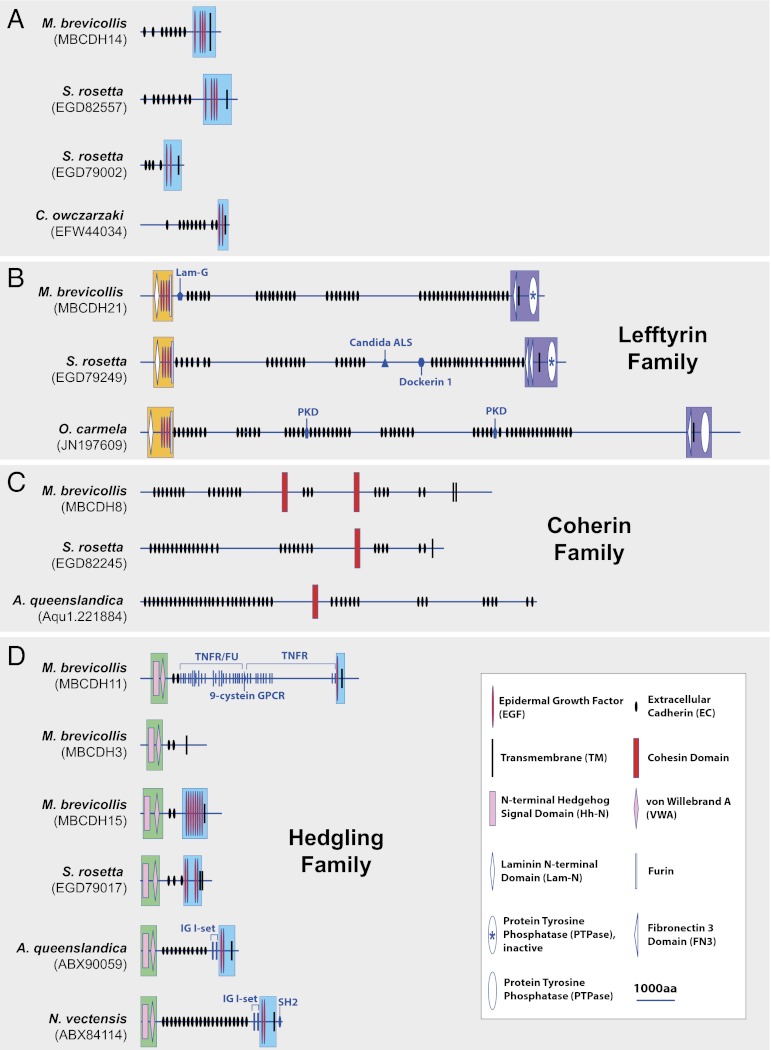
Fig. 2.
Predicted domain architecture of modern representatives of premetazoan cadherins. At least three cadherin families evolved before the origin of metazoans. (A) The single cadherin discovered in the genome of C. owczarzaki has a cassette of EGF repeats positioned proximal to a single transmembrane domain (blue box) that is also found in choanoflagellate and sponge cadherins. The phylogenetic relationships among cadherins with this feature are not yet clear. The lefftyrin (B) and coherin (C) families are present only in choanoflagellates and sponges. Lefftyrins are distinguished by an N-terminal “LEF” cassette (orange box) with a Lam-N domain, four EGF repeats, and a Furin repeat and a C-terminal “FTY” cassette (purple box) with one or two Fibronectin 3 domains, a transmembrane domain, and a tyrosine phosphatase domain. Coherins contain a diagnostic bacterial/archaeal-like cohesin (50) domain. (D) The hedgling family (1, 26) is present in choanoflagellates, sponges and cnidarians and is absent from bilaterians. All hedglings contain an N-terminal Hedgehog signal domain linked to a von Willebrand A domain (green box) and most contain a series of EGF repeats proximal to the transmembrane domain (blue box). Candida ALS, Candida Agglutinin-like sequence; IG I-set, Ig I-set; KU, BPTI/Kunitz family of serine protease inhibitors; Lam-G, Laminin G domain; 9-cystein GPCR, 9-cystein G protein coupled receptor; PKD, polycystic kidney disease; SH2, src homogy domain 2; TNFR, tumor necrosis factor receptor.