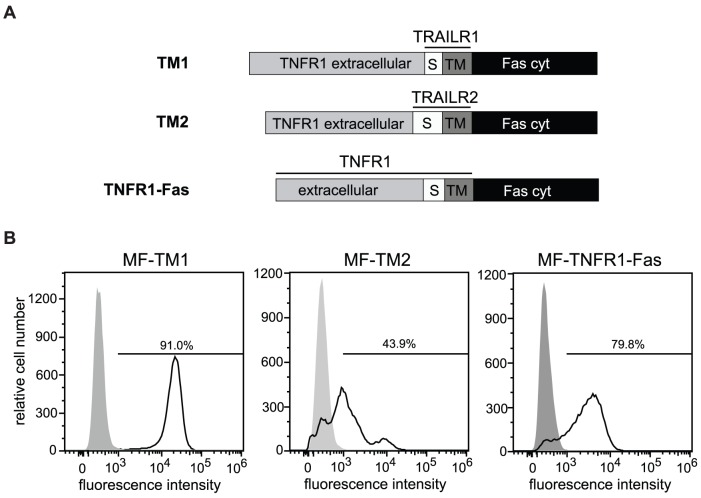
Figure 4. Receptor chimeras with identical ligand binding sites and intracellular signaling domains.
A. Schematic representation of TNFR1-TRAILR1-Fas (TM1), TNFR1-TRAILR2-Fas (TM2) and TNFR1-Fas chimeric proteins. TNFR1-Fas receptor was established through the fusion of the cytoplasmic domain of Fas, amino acids 191–335, to the C-terminus of the potential transmembrane region of TNFR1 (amino acid 236). In TM1 and TM2 receptor chimeras the stalk (S) and transmembrane (TM) regions of TNFR1 (aa 197–234) were then substituted with the corresponding regions of TRAILR1 (amino acids 230–262) or TRAILR2 (amino acids 179–231). B. Immortalized mouse fibroblasts were stably transfected with TM1, TM2 and TNFR1-Fas expression plasmids. Expression of the chimeras was analyzed by flow cytometry using TNFR1-specific antibodies. Percentage of positive cells is indicated.