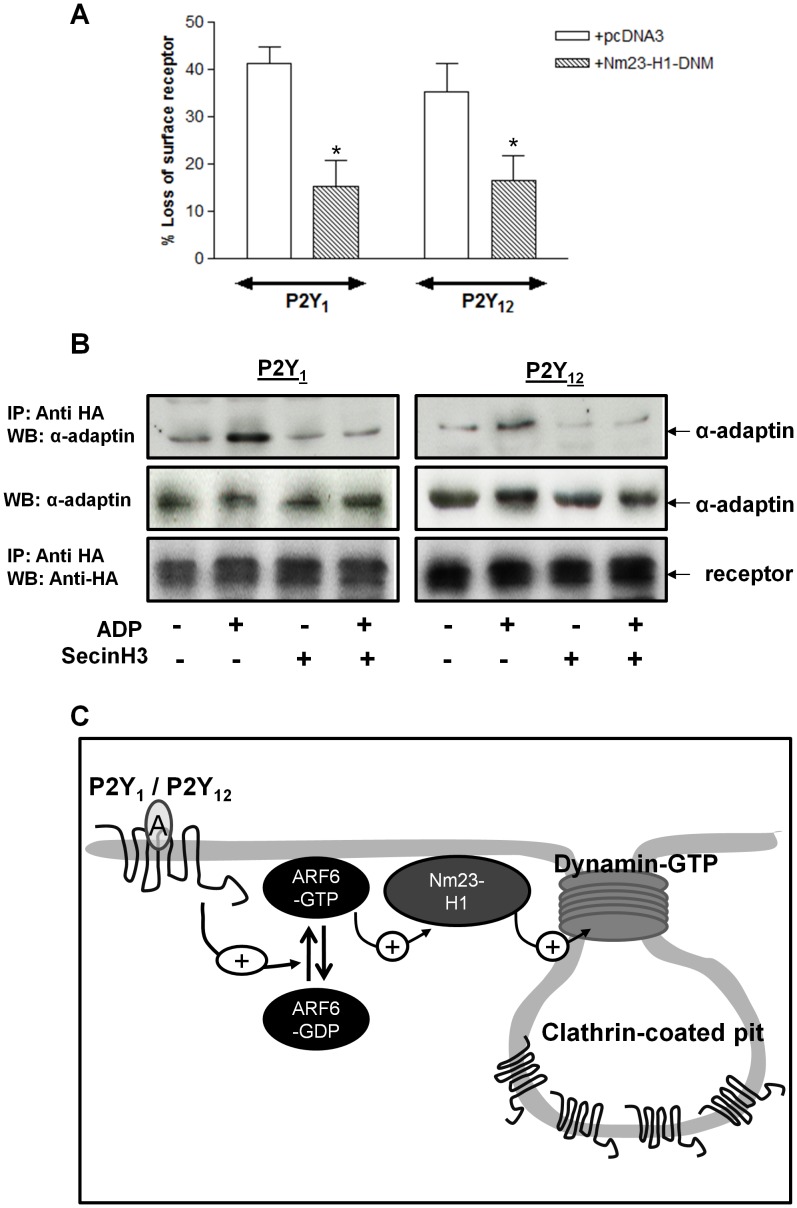
Figure 7. ARF6 regulates aspects of clathrin- and dynamin-dependent P2Y1 or P2Y12 purinoceptor receptor internalization.
(A) 1321N1 human astrocytoma cells stably expressing either HA-tagged P2Y1 and P2Y12 purinoceptor were transfected with a dominant negative mutant of the Nucleoside diphosphate kinase Nm23-H1 (H118C Nm23-H1). Cells were subsequently treated with ADP (10 µM; 30 min) and surface receptor loss assessed by ELISA. The data represent mean ± SEM of four independent experiments. *p<0.05 compared with pcDNA3 vector control (Mann–Whitney U-test). (B) 1321N1 human astrocytoma cells stably expressing either HA-tagged P2Y1 and P2Y12 purinoceptor were treated with SecinH3 (15 µM) for 30 minutes. Cells were subsequently stimulated with ADP (10 µm; 5 min) at 37°C. Reactions were stopped by addition of ice-cold lysis buffer and receptor was immunoprecipitated from cell lysates using an anti-HA antibody (HA-11) and association with endogenous α-adaptin assessed by immunoblotting. Whole-cell lysates (WCL) lanes are included as positive controls for detection by anti-α-adaptin antibodies as are lanes showing equal levels of receptor immunoprecipitation. (C) Model of ARF6-dependent internalization of P2Y1 and P2Y12 purinoceptor. Activation of the P2Y1 and P2Y12 purinoceptor increases ARF6 activation. ARF6-GTP in turn stimulates Nm23-H1 which in turn promotes dynamin-dependent internalization of the P2Y1 and P2Y12 purinoceptors.