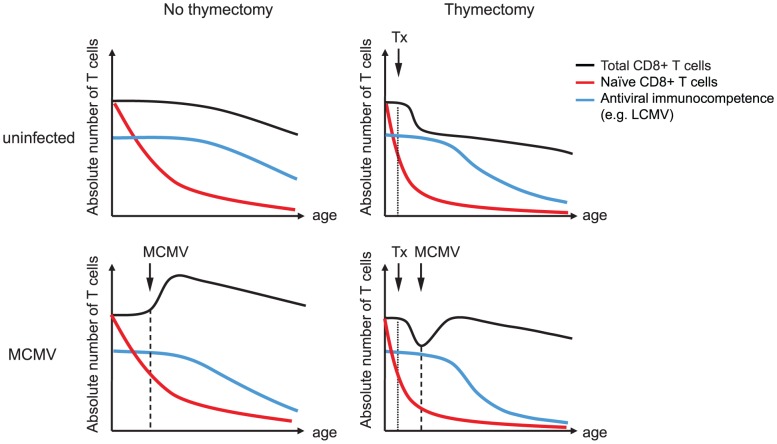
Figure 8. Integrative model of the influence of MCMV-infection, ageing and thymectomy on CD8+ T cell populations and protective immunity.
Ageing is accompanied by a slow but progressive decline of the total (black line) and the naïve (red line) CD8+ T cell pool. Immune senescence is characterised by an age-associated reduction of immunocompetence (blue line), particularly against newly encountered antigens (e.g. LCMV). Tx of young mice leads to a substantial and rapid shrinking of the naïve T cell compartment reducing the number and the diversity of naïve T cell precursors on top of ageing. Tx also reduces the total CD8+ T compartment, which is later affected by an age-associated decline. MCMV-infection results in an immediate and persistent expansion of the total CD8+ T cell compartment whereas the naïve T cell pool remains intact. Nevertheless, MCMV-infection contributes to reduced immunocompetence over time, possibly by an enhanced competition of massively expanded CMV-specific Tem with newly generated effector cells. In old Tx mice with latent MCMV-infection, immuocompetence is cumulatively affected by the restricted naïve T cell pool and by the increased competition of CMV-specific Tem.