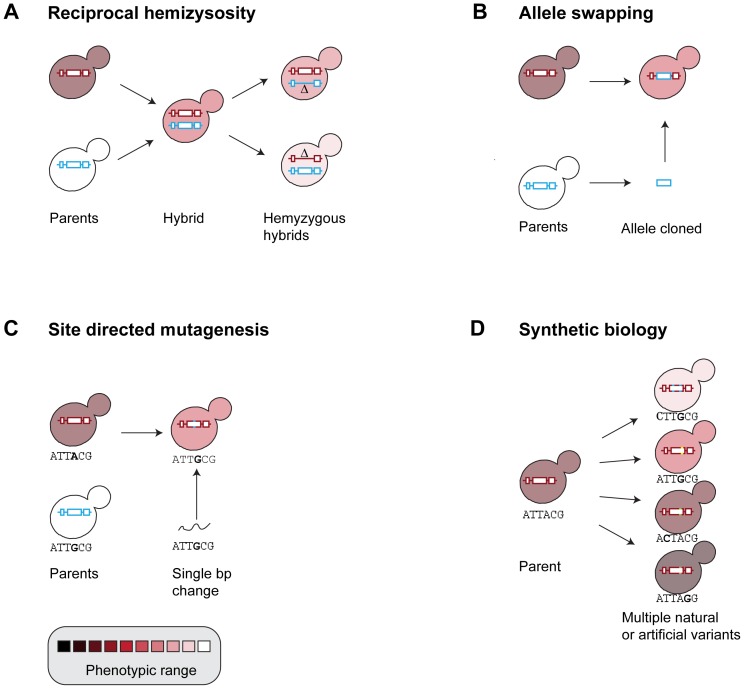
Figure 1. Experimental measures of natural variation.
Yeasts offer a unique opportunity to engineer changes to measure the impact of phenotypic variants on traits. (A) Reciprocal hemizygosity has high throughput and can be used to test a large number of candidates. Hybrids that differ only in which of two alleles is present/deleted are compared. Deletion collections of multiple strains will soon be available allowing genome-wide systematic studies using hybrids to test all candidates easily or even for discovery of phenotypic effects directly. (B) Allele swapping is less high throughput but allows testing phenotypic effects of specific alleles in different genetic backgrounds. This is more precise than reciprocal hemizygosity. (C) Site-directed mutagenesis is a rapid and precise way of testing known and novel base changes for phenotypic effects. (D) Synthetic biology has the potential of simultaneously testing multiple variants, both natural or artificial, in a single gene [55] or scattered through the genome [47].