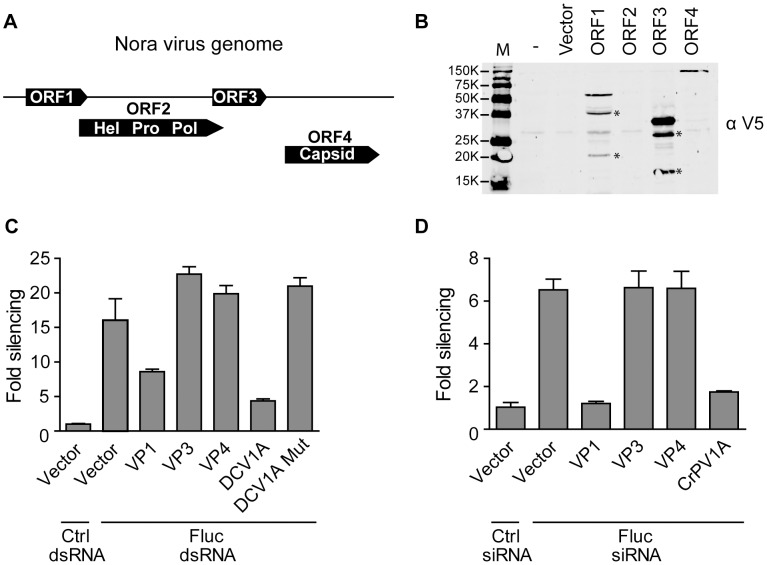
Figure 2. Nora virus VP1 suppresses RNAi in vitro.
(A) Schematic representation of the Nora virus genome with its four predicted ORFs in three different reading frames. There is a 7-nt overlap between ORF1 and ORF2 and a 26-nt overlap between ORF2 with ORF3. An intergenic region of 85 nt separates ORF3 and ORF4. (B) Western blot analysis of V5-epitope tagged Nora virus expression constructs. Two days after transfection of the indicated plasmids into S2 cells, expression of the constructs was analyzed by Western blot using the V5 antibody (αV5). Asterisks (*) indicate additional bands that do not correspond to the expected size of the full-length protein product. (C) RNAi reporter assay in Drosophila S2 cells. Copper-inducible plasmids encoding Fluc and Rluc were transfected into S2 cells together with a construct expressing Nora virus ORF1, 3, and 4, encoding viral protein 1 (VP1), VP3, and VP4, respectively. Two days after transfection, dsRNA targeting Fluc or GFP (Ctrl) was added to the medium. Seven hours later, expression of FLuc and Rluc was induced and luciferase activity was measured the next day. FLuc counts were normalized to Rluc counts and presented as fold silencing relative to the control GFP dsRNA. Plasmids encoding DCV 1A and the K73A mutant (DCV 1A mut) were used as controls. (D) siRNA-based RNAi reporter assay. The experiment was performed as described in panel C, but 21-nt Fluc siRNAs were cotransfected with the reporter plasmids to silence gene expression. An siRNA targeting the human MDA5 gene was used as a non-silencing control (Ctrl). Bars in panel C represent averages and standard deviations of five independent samples; bars in panel D represent averages and standard deviations of three independent samples. Panel C and D are representative for two and three independent experiments, respectively.