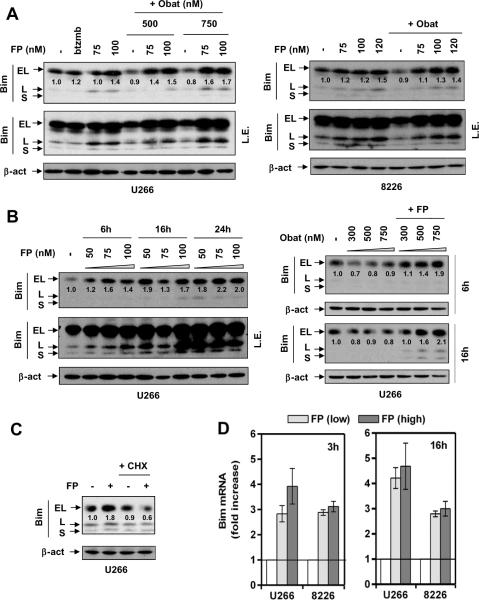
Figure 3. FP induces Bim expression at the transcriptional level.
(A) U266 cells were exposed (24 hr) to 75 – 100 nM FP +/− 500 – 750 nM obatoclax, or 4 nM bortezomib for comparison (left); RPMI8226 cells were exposed (24 hr) to 75 – 120 nM FP +/− 750 nM obatoclax (right). (B) U266 were incubated with 50 – 100 nM FP for 6, 16, and 24 hr (left); or 300 – 750 nM obatoclax +/−100 nM FP for 6 and 16 hr (right). (C) U266 cells were treated with 100 nM FP +/− 1 μM CHX for 24 hr. After drug treatment, immunoblot analysis was performed to monitor protein expression of three isoforms (EL, L, and S) of Bim. For changes in BimEL protein levels, the density of blots was quantified; values reflect the ratio of integrated densitometric determinations between untreated and drug-treated cells, with normalization against β-actin. L.E. = long exposure. (D) Cells were exposed to low (U266, 75 nM; 8226, 100 nM) or high (U266, 100 nM; 8226, 120 nM) concentrations of FP for 3 hr and 16 hr, respectively, after which quantitative RT-PCR was performed to determine mRNA levels of Bim, using β-actin as control.